“Overweight or obese pregnant women are likely to risk the later spans of life of their offspring with threatening health problems.” – concludes the latest research finding of DORIAN, a paramount obesity project of Europe funded by European Commission.
Developmental Origins of Healthy and Unhealthy Ageing: The Role of Maternal Obesity (DORIAN) supported by The Seventh Framework Programme works towards research into vital health related areas such as prevention and disease management strategies, biomedical advances, and age-related and healthy aging illnesses.
Another important element of this report was the significance of preventing excessive weight gain in women of child bearing age and adult girls to avoid maternal obesity leading to severe health problems in the later stages of life of their babies. This particular finding was developed from a research by Finnish research center of University of Helsinki and Folkhalsan Research Centre in Helsinki.
“The project has underlined the importance of preventing obesity in pregnancy, preventing excess weight gain during pregnancy, and also maintaining healthy diet without too much fat – all of which can have short and long term effects on the health of the mother and her child,” said Institute of Clinical Physiology’s Dr. Patricia Iozzo from Pisa, Italy.
Health Problems Passed from Overweight Mothers
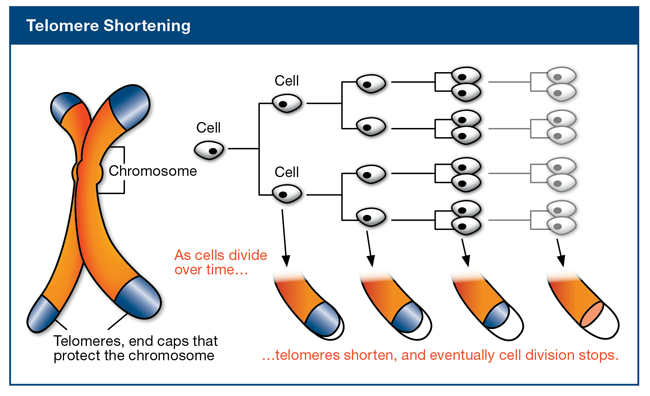
1. Shorter telomeres:
Getting progressively shorter with age, telomeres are the protective caps or ends on the end of a chromosome which help in cell division without the threat of losing genes. They also refrain chromosomes from fusing or fraying with other chromosomes and eventually corrupting the cell’s genetic blueprint. Problems due to shorter telomeres could be aging, premature aging, cancer, Alzheimer’s disease, and intestinal diseases, hardening of arteries, poor wound healing, high blood pressure, softening of bones, life-threatening infections, etc., due to dyskeratosis congenita.
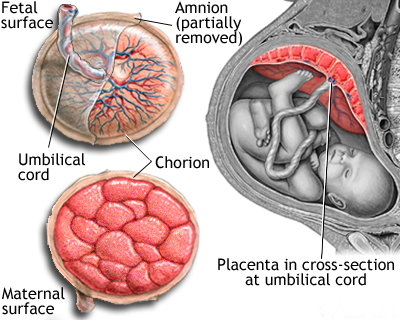
2. Weakened placenta:
Placenta is an organ that develops during pregnancy close to the womb’s lining which protects the fetus from infection and harmful hormones like stress hormones viz., cortisol and glucocorticoids. When pregnant women take high fat diet, the placenta begins to become weak to protect the unborn baby’s development and growth from getting damaged or hindered due to unwanted factors such as the stress hormone cortisol, which could affect the development of fetal brain. Pregnant women who consume drugs, alcohol, nicotine, and other harmful products can also risk the life of their fetuses as the placenta weakens. With reduced growth, the child may also suffer from mood disorders in the later stages of his life.
3. Other problems:
Type 2 diabetes, heart diseases like cardiovascular disease, stroke, and cerebrovascular disease, and depression.
The old saying “eat for two” can put at stake not only the mother’s life but also of the baby.
Dr. Iozzo continued, “In the context of maternal-offspring health, attention should be devoted to the prevention of overweight and obesity among young girls, representing ‘tomorrow’s mothers’. Targeted strategies are also needed to ensure pregnant women do not add excess weight and protect their physical and mental health, and that of their children.”
A study reveals that children who were born to mothers with healthy weight during pregnancy are less prone to diseases than those born to overweight mothers. Director of Royal College of Midwives, Louise Silverton has the same views on maintaining the right weight during pregnancy. “This report adds more to our knowledge about the importance of the environment in which the fetus is nurtured. After birth, women need support to develop healthy patterns of eating and exercise for themselves and their family. For women who are overweight or obese they need support and signposting to access weight-loss services to ensure that they are an ideal weight before they embark on their next pregnancy.”
Healthy Lifestyle for Pregnant Women
1. Avoid contact with animals:
This is important as you may be infected with toxoplasmosis, listeriosis, or chlamydia. Animals and pets like lamb, cat, dog, sheep, etc., should be kept away from pregnant women.
2. Say no to alcohol, drugs, and smoking:
Smoking could lead to stillbirth and premature labor, street drugs can cause miscarriage, low birth weight, slow growth, serious uterus bleeding, etc., and alcohol could weaken placenta causing brain damage, impaired intellect, facial malformations, and many other complications to the fetus.
3. Preferably avoid sex:
In case of heavy bleeding and waters been broken during pregnancy, having intercourse could amplify the risk of infection. Besides, the pregnant woman could experience Braxton-Hicks contractions due to orgasm and sex which can be uncomfortable, also making the bump feel hard.
4. Consider muscle strengthening + aerobic physical activity:
You should always consult your obstetrician before enrolling into any such exercising programs. Having said that, 30 minutes of exercising activity is highly recommended for pregnant women.
5. Take your maternity leave:
You should have a word with your employer if your job would possibly pose a risk to your or baby’s health when you’re pregnant or planning to have a baby.
Healthy Diet for Pregnant Women
1. Carbohydrates and starchy foods:
Containing fewer calories, these foods are quite satisfying for your stomach and also rich in fiber, vitamins, and energy. The sources could be cornmeal, pasta, unsweetened cereals, potatoes, millet, oats, etc. It is advised to opt for wholemeal in place of processed varieties.
2. Dairy products:
These are important during pregnancy provided they have low fat content. Go for red-fat hard cheese, semi-skimmed milk, low sugar or low fat yoghurt. Fromage frais and cheese are also nutritional dairy varieties; however, you need to avoid soft blue cheeses and soft cheeses with white rinds.
3. Vegetables and fruits:
5 portions of a variety of these foods are highly recommended as they are rich in minerals and vitamins. Consume dry fruits like figs, dates, currants, etc., pulses, beans, sweet potatoes, turnips, swedes, parsnips, pulped fruits, fruit/vegetable juices (1glass/day only), salad vegetables, soups, and puddings.
4. Protein foods:
Choose cooked lean meat (without skin and liver) including beef, lamb, etc. You should consider eating 2 portions of fish in a week where one of them could be oily fish (mackerel, sardines, or salmon). Intake of tuna should be restricted to no more than 140 grams a week. Take heed that you avoid eating marlin, swordfish, shark, and other wild fishes when you’re pregnant.
5. Folic acid, calcium, and iron:
Foods that are rich in these elements should be regularly consumed. Brown rice, green vegetables, and fortified cereals contain a good amount of folic acid while iron is richly present in dried fruits and red meat. Calcium is plenty in dairy products.
6. Avoid certain foods:
Do not eat fizzy drinks, pastries, spreading fats, chocolate, cake, biscuits, cream, oils, crisps, salad dressings, and other foods containing high amounts of sugar, calories, vitamin A, listeria, liquorice, caffeine, and saturated fats.