Proper nutritional food and diet is the most important requirement during pregnancy. Healthy and nutritional food is required to ensure proper growth and development of the baby. These foods provide energy to the baby and the mother and ensures the mother has sufficient energy to deal with the changes that are occurring.
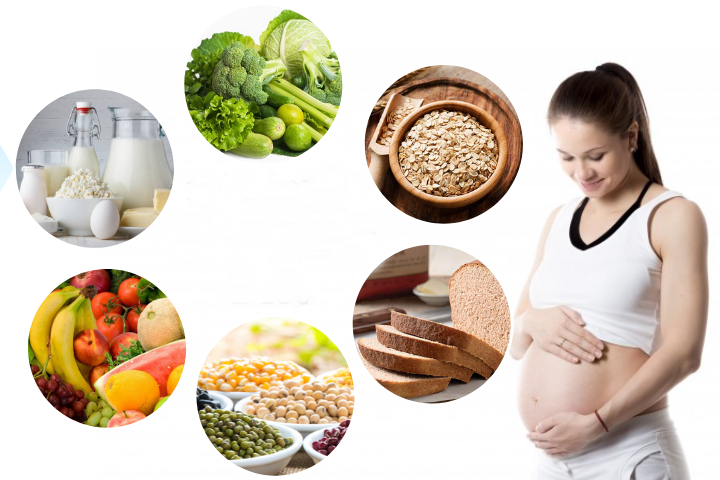

Healthy diet is a vital part of a healthy lifestyle, and more so when you are pregnant. The diet needs to be perfectly balanced with the right amount of nutrients and minerals. This is crucial for the baby’s growth and development. A healthy and nutritious diet reduces the chances of complications and problems in pregnancy.
Certain foods are recommended to pregnant women while some are not. Good nutritional diet has many benefits. It can help manage mood swings, balance emotions, minimizes morning sickness, reduces risk of anemia, contributes to healthy fetal development, and reduces the risk of birth defects.
There are some things you should know about which foods are good for you and the baby and which foods you need to avoid.
What to Eat During Pregnancy?
1. Diary products:
These include milk, cheese, and yogurt. However, it is important to ensure that whatever dairy product you consume should be pasteurized. These foods are good sources of vitamin D, calcium, and proteins. They are essential for proper development of the baby’s bones, teeth, muscles, heart, nerves, and for blood clotting. Consuming at least 4 servings a day is often recommended.

2. Protein:
Pregnant woman should eat a protein rich diet to support the baby’s growth and development. This includes food items like meat, eggs, fish, cheese, tofu, milk, etc. Protein rich diet in pregnancy reduces the risks and chances of low birth weight of the baby. It can also prevent muscle fatigue, fluid retention, and frequent infections.

3. Fruits and Vegetables:
Fruits and vegetables provide all the important nutrients and vitamins essential for the growth and development of the baby as well as maintaining the mother’s good health. These fruits and vegetables also help in managing nausea and vomiting during pregnancy. Fruits like apricots, oranges, mangoes, pears, pomegranates, avocados, guava, etc. are the best way to boost vitamin intake as well as satisfy sugar cravings.

Vegetables like broccoli, dark leafy vegetables, etc. contain many nutrients, fiber, vitamins like vitamin C, K, and A, calcium, iron, folate, etc. that are essential for pregnant women. These vegetables are also a good source of antioxidants. Folate rich vegetables such as broccoli, spinach, kale, asparagus, Brussels sprouts, and peas, should be consumed by the mother as folate plays an important role in protecting the fetus against neural tube defects.
4. Lean meat:
Lean meat is low fat meat and is rich in iron and is critical in the development of red blood cells supply in baby as well in the mother. Iron also helps in strengthening the nerve connections and thereby developing the baby’s brain. The leaner the cut, the more protein it contains.

5. Whole Grains:
Breads provide the essential carbohydrates required by the mother during pregnancy. Starchy food products such as bread, potatoes, pasta, rice, and cereals should make up to about one third of the diet of the expecting woman. These food items provide the energy that is essential during pregnancy. These carbohydrates are also important source of fiber, iron, and B vitamins. Carbohydrates are important component of food that make up the healthy diet that is recommended during pregnancy.

High quality carbohydrate containing food such as wholegrain bread, yogurt, vegetables, and fruits are recommended during this period. It is also advised that low quality carbohydrate foods should be kept at a minimum.
6. Vitamin Supplements:
Eating a well balanced and nutritious diet provides all sorts of minerals and vitamins required during pregnancy. But it is equally important to take folic acid supplements if you are pregnant or planning to be. Approximately 400 micrograms of folic acid supplements are recommended to be taken by the woman everyday from the period before she is pregnant to up to 12 weeks of pregnancy. Folic acid supplements are essential to avoid the risk of neural tube defects and developmental defects in the baby.

Similarly, 10 micrograms of vitamin D is required by pregnant and breastfeeding women to regulate the amount of calcium and phosphorus in the body. It is essential for keeping bones, teeth, and muscles healthy. Vitamin B and C supplements are also recommended. Iron supplements are also advised to women who are anemic during pregnancy.
As there is a list of must haves during pregnancy, there is also a long list of don’t haves, some of which are mentioned below.
What to Avoid During Pregnancy?
1. Raw and Under-cooked Food:
Raw and under-cooked food may cause toxoplasmosis as the Toxoplasma parasite lives and grows around the area where vegetables and fruits grow. Consuming unwashed vegetables and fruits may increase the risk of ingesting these harmful microbes. This can cause food poisoning, fever, muscle pains, etc. This infection can severely harm the baby and interfere with its development.
2. Unpasteurized Dairy Products:
It is unsafe to consume raw milk or unpasteurized dairy products during pregnancy. Raw and unpasteurized milk and products have a higher risk of food borne diseases. Bacteria such as salmonella, E. coli, etc. are present and may cause harm to both, the mother and the baby.

Pasteurization subjects the milk to higher temperature, thereby effectively killing the harmful micro-organisms present. Hence, it is advisable to drink pasteurized milk and consume pasteurized dairy products. Alternatively, you can also use non-dairy milk like soy milk, almond milk, oat milk, etc. as they contain the same nutritional value.
3. Raw or Under-cooked Eggs:
Raw or under-cooked eggs possess a higher risk of Salmonella. Hence, eggs should be cooked until the yolk and egg white are cooked hard. Foods made using raw eggs such as mayonnaise, hollandaise sauce, mousse, etc. should also be avoided.
Always check the labels on eggs for pasteurization mark and cook all the egg and egg products at a high temperature to reduce the risk of infections.
4. Soft Cheese:
Soft cheese has higher risk of containing Listeria bacteria that causes potentially harmful infection, listeriosis. This infection can lead to miscarriage or premature delivery. If this infection occurs in the later stages of pregnancy, it can harm the baby. The solution to this is heating the cheese at higher temperatures, until its bubbly and melts, to kill the bacteria present. Check for pasteurization label to avoid risks of infections.
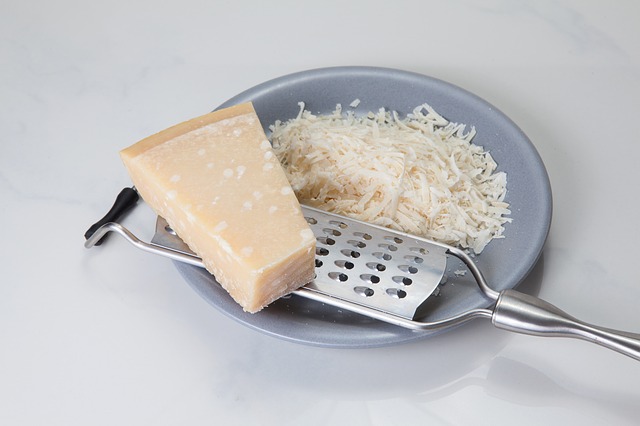

Soft mould cheese like Brie, Camembert, and certain goat cheeses are best to be avoided during pregnancy. Hard cheeses such as cheddar are recommended.
5. Caffeine:
Consuming too much coffee or caffeinated beverages during pregnancy have been linked to premature delivery and low birth weight of the infants. It has also been reported that women who consumed more than 200 milligrams of caffeine had increased risks of miscarriages. So, coffee and caffeine intake should be limited to avoid any possible complications.

6. Alcohol:
Alcohol is not safe in any stage of pregnancy. Women should stop drinking alcohol when they find out they are pregnant and even before that. Drinking alcohol during pregnancy can lead to developmental defects in babies. Reports suggest that alcohol consumption during the first trimester of pregnancy can lead to facial deformities in babies. Certain reports also suggest mental birth defects in babies whose mother consumed alcohol during pregnancy.
7. High Mercury Fish:
Fishes such as king mackerel, shark, swordfish, etc. contain high levels of mercury and are often recommended to avoid eating during pregnancy or nursing. This is because high levels of mercury can harm the baby and may lead to brain developmental defects, hearing and vision problems, and can also affect the lungs and kidneys.
Eating raw or under-cooked shell fish such as oysters should also be avoided as it can lead to food poisoning.

Similarly eating any raw or rare cooked meat is inadvisable as it increases the chances of toxoplasmosis which can lead to mental disability, blindness, and certain other complications in the baby.
The most important time to have a balanced and nutritious diet in life is before, during, and after pregnancy. Nutritionists believe that the best source for an expecting mother to receive her nutrients and vitamins is from her diet and hence, following the guidelines on what to eat and what to avoid is important. The guidelines are simple and easy to follow and will ensure the pregnancy is a smooth ride and the baby is healthy and happy.



 Likewise, signs like a bluish tint in the fingernails, skin, and lips, fast breathing and shortness of breath while breast-feeding, are the signs that suggest congenital heart defects in babies. Also, if the hole in the heart is small, it may not show any symptoms.
Likewise, signs like a bluish tint in the fingernails, skin, and lips, fast breathing and shortness of breath while breast-feeding, are the signs that suggest congenital heart defects in babies. Also, if the hole in the heart is small, it may not show any symptoms.