Gallbladder is a small pear shaped organ which is located beneath the liver and is part of the digestive system. Along with the pancreas, liver, bile duct and hepatic duct, the gallbladder is a part of the hepato-biliary system. Gallstone is a health disorder occurring due to the formation of solid stones inside the gallbladder. Significant metabolic disturbances lead to gallstone formation.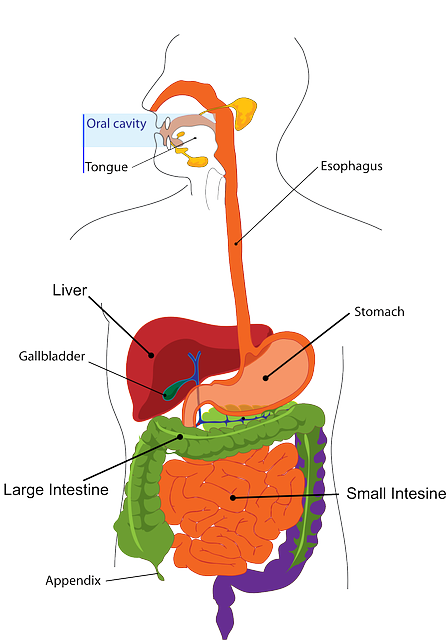
Gallbladder plays a vital role in the metabolism and assimilation of fats. Therefore, any disturbances in the physical or physiological functioning of gallbladder, leads to faulty fat metabolism. Stone formation is one of the commonest disorders of the gallbladder. This article explains in the detail about the cause, symptoms, diagnosis and treatment of gallstone.
Causes of Gallbladder Stone
Gallbladder produces and secretes a digestive juice known as bile. It helps in metabolizing fats. Sluggish flow of bile often causes its components to deposit and harden within the gallbladder. These hardened deposits are termed as gallstones. Contributing factors to gallstone formation are mentioned below.
1. Components of Bile
Oxalate, calcium, cholesterol, bilirubin, are some of the key components of bile. Elevated levels of either of these components is a major causative factor for the formation of gallstones.
2. Other Health Disorders
Any disorder which increases the levels of bilirubin circulating in the system, indirectly leads to formation of gallstones. Polycythemia Vera, sickle cell anemia, jaundice, hepatocellular inflammation, are commonly responsible for gallstones.
3. Lack of Exercise
Exercise is the best way to keep diseases at bay and maintain good health. It helps in maintaining good muscular tone, blood circulation and a healthy metabolism. Lack of exercise leads to loss of healthy muscle tone which is an important contributing factor to the formation of gallstone.
When the gallbladder muscles are well toned, it helps in maintaining an adequate flow of bile. This prevents stasis of bile and subsequent gallstone formation. People who tend to have sedentary lifestyle and indulge in little physical activity are more likely to develop gallstone than people who are physically active.
4. Unhealthy Diet
Cholesterol levels are important in determining how healthy a person’s fat metabolism is. Consumption of empty calories and junk food leads to accumulation of ‘bad cholesterol’ in the body tissues. This affects the person’s fat metabolism in a harmful way.
Excess accumulation of cholesterol enhances the possibility of gallstone formation. In order to keep cholesterol levels in check, junk food, fried food, food packed with excess calories, should be avoided. It is important to include salads, fruits, fiber rich food etc. in the daily diet.
5. Gender
Statistically, women are more likely to develop gallstone than men. While there is no medical evidence to pinpoint towards a specific cause, this is believed to be due to women’s menstrual cycle.
Estrogen is the dominant hormone in the female body. It increases the levels of blood cholesterol, thus contributing to gallstone formation. Proportion of estrogen is negligible in men as compared to women. Therefore, men are at a much lower risk of developing gallstone.
6. High B.M.I
Medical studies have revealed that people who have B.M.I above 30 are more likely to develop gallstones. B.M.I is directly related to a person’s body weight and height. Greater the person’s weight, higher is the B.M.I.
Overweight and obese people have higher B.M.I due to their weight. They also tend to have unhealthy cholesterol deposits in their bloodstream. This leads to formation of gallstones.
Other contributing factors for developing gallstone include immunity, daily diet, lifestyle, stress levels, social environment etc. It is important to remember that people who do not fit into either of the above mentioned criteria may also develop gallstones.
Symptoms of Gallstone
The importance of good health is not realized till the onset of any disease. Patients themselves observe the earliest sign of ill health, even before a doctor can notice anything wrong. These signs can be in the form of externally visible changes or subtle changes experienced by the patients only. The commonest signs of ill health experienced by patients suffering from gallstones are mentioned below:
1. Indigestion
Sluggish flow of bile takes its toll on the digestive system. Indigestion in the form of nausea, vomiting, altered appetite, altered bowel habits, may be experienced by patients suffering from gallstones. Patients often complain of lack of desire to consume any food. Spicy food, oily food, food rich in carbohydrates, tends to be troublesome for patients.
2. Bloating
Bloating is another complication caused due to sluggish flow of bile. Since food cannot be digested at its usual pace, there is increased gas formation in the intestines, leading to bloating. Patients will often complain of heaviness in the abdomen after a meal. Taking a walk or performing light physical activity often provides comfort from these symptoms.
3. Abdominal Pain
Abdominal pain could be dull and constant in nature, or sharp and spasmodic. Pain occurs primarily due to inflammation in and around the gallbladder. Pain is felt more often in the right upper part of the abdomen. Patients are also known to complain of abdominal pain radiating up towards to right shoulder. Sudden increase in the intensity of pain can be attributed to torsion of the gallbladder in an effort to expel the stones.
4. Jaundice
Jaundice is a set of symptoms commonly occurring in patients with hepatobiliary dysfunction. Patients with gallstones often complain of yellowness of skin and mucus membranes accompanied by dark yellow pigmentation of urine.
Presence of all or any few of the above mentioned signs and symptoms prompt a visit to the doctor. Patients may also present with signs and symptoms other than those mentioned above. Along with diagnostic tests and the doctor’s examination findings, patients’ own symptoms help in confirming the presence of gallstones.
5. Silent Gallstones
Silent gallstones is a condition wherein, patients do not experience any symptoms or discomfort despite presence of gallstones. Gallstones may be detected during a routine health check up or while undergoing diagnostic scan for any other health condition. However, despite absence of symptoms, patients need to be watchful of their health.
Diagnosis of Gallstones
1. Physical Examination
When patients present with symptoms of gallstones, doctors confirm the diagnosis using their own medical skills. A detailed physical examination of the patient reveals certain findings that are characteristic of gallstones. Some of these findings are mentioned below:
- Tenderness and pain experienced by patient on palpation of the abdomen
- Yellowness of skin and mucus membrane
- Discoloration of tongue
- Elevated body temperature may be observed in some patients
The final step to confirming diagnosis of gallstones includes certain diagnostic tests.
2. Diagnostic Tests
Blood tests and scans are often advised to patients who are suspected to be suffering from gallstones. Blood tests reveal elevated levels of white blood cell count and CRP (C-reactive protein).
Scans like USG are useful in confirming presence of gallstones. USG helps in determining the number as well as dimensions of the gallstones. MRI scan and CT scan may be ordered if patients present with any health complications or do not respond well to treatment.
These tests and scans are utilized not only for primary diagnosis of gallstones but also during follow ups, to determine how well patients respond to treatment.
Treatment of Gallstone
The mode of treatment for gallstones depends on the number and dimension of gallstones and intensity of symptoms. Following treatment options are offered by doctors:
1. Medicinal Treatment
Medicines are prescribed to offer relief from symptoms of gallstones and not to get rid of the stones. Pain killers, anti-inflammatory medicines, antacids, anti-flatulent medicines, anti fever medicines, are commonly prescribed to patients.
Patients who have been diagnosed with gallstones but do not require immediate surgical treatment, are often treated using oral medicines only.
2. Surgical Treatment
Cholecystectomy or gallbladder removal surgery is advised to patients as a mode of treatment for gallstones. Patients experiencing recurrent gallstones or health complications due to gallstones are often advised to undergo surgery.
Gallbladder removal surgery tends to affect the patient’s digestive functions in long run. However, those effects can be taken care of with regular medication and diet.
3. Lifestyle Modification
Patients with silent gallstones do not require immediate medicinal or surgical treatment. However, they need to be careful about their health and may be asked to make minor changes in their day to day habits.
It is important to take care of diet and exercise in order to maintain good health. Avoiding junk food, consumption of empty calories, food that is heavy to digest is advised to patients. It is important to indulge in regular physical exercise to maintain good health.
Gallstones if left untreated may cause complications which could require further treatment. Patients are advised to seek medical help promptly, should they experience any of the symptoms of gallstones. Further diagnosis and treatment should be initiated only after consulting with a physician or gastroenterologist.