Hearing is a wonderful gift of the nature bestowed upon mankind. Externally we merely see two ear lobes which receive all the sound in our surroundings and help us to hear. But within, is an extremely intricate and complex network of bones, muscles, membranes, nerves which help to conduct the sound waves to the brain and actually help in perceiving the sound and noise.
But what will happen if we are not able to perceive noise and sound? Even this thought is frightening, isn’t it? However, such situations may arise, leading to loss of hearing ability. This is when doctors will recommend tests to check your hearing capability.
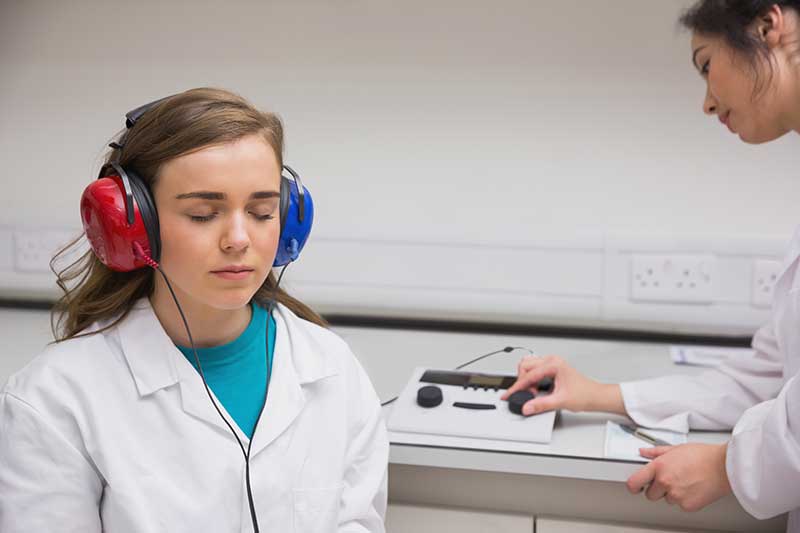

One of the investigative tests done to assess presence and intensity of hearing loss is Audiometry Test. Audiometry test is affordable at cost. It can also be done for patients experiencing tinnitus (buzzing sound in the ears) and dizziness.
Before getting into details about audiometry, let us first understand some basics of the ear.
Basic Anatomy of the Ear:
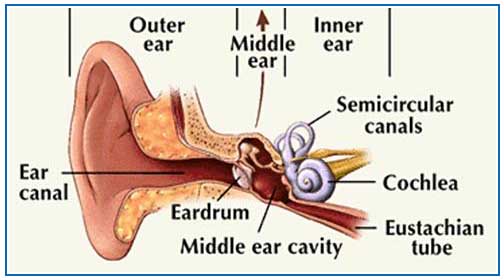
The ear is divided into the external ear, the middle ear and the internal ear. External ear comprises of ear lobes. Middle ear is comprised of a thin membrane known as the tympanic membrane or ear drum. This is first in the line of internal chain of organs which help in conducting sound to the brain. When sound passes through this membrane, it vibrates. Just behind this membrane are three small bones viz. malleus, incus and stapes. As the eardrum vibrates, the three bones move accordingly as well and conduct the sound forward into the auditory canal. At the base of stapes is another membrane known as oval window.
The inner ear begins from the oval window. It continues within in the form of a vestibule, three semicircular canals which are arranged at right angles to each other and a spiral bony structure known as cochlea. All these are membranous structures and the membrane extends inside the spiral bony cochlea.
Apart from these structures, there are two fluids, endolymph and perilymph present within the inner ear. They also aid in maintaining normal hearing. After passing through the ear, the sound waves stimulate nerves which generate a signal that travels to the brain. Many blood vessels and nerves are responsible for aiding the function of ear.
Any disturbance in the structure or function of any of the above mentioned organs, leads to diminished hearing.
Why is it essential to perform Audiometry?
As mentioned earlier, audiometry is one of the investigative tests which is helpful in determining any abnormality in the auditory system. Following are the indications that an audiometry is necessary:
-
Hearing difficulties:

Hearing-Difficulty
Normal hearing may suddenly diminish or completely reduce because of impacts like physical trauma due to insertion of something sharp into the ears, something hitting the ear hard, sudden loud noise, recurrent exposure to noise of very high intensity, infection of the ear, diseases of nerves or bones of the ear.
-
Tinnitus:

Tinnitus
Tinnitus is a buzzing sound which can be felt in the ears after sudden trauma or exposure to extremely loud noise. Other causes of tinnitus can be damage to nerves which are associated with the function of hearing. These factors damage one of the components of the entire hearing apparatus. This damage can be detected with help of audiometry.
-
Age related deafness:
Age-Related-Deafness
With advancing age, natural degeneration of all tissues in the body begins. The nerves, membranes and bones involved in the function of hearing will also be affected due to aging. This could lead to hearing loss which is commonly observed in people as they cross their 60s.
If patients have history of any of the above, it is advisable for them to consult with a doctor immediately. This could be the beginning of some deep seated ear problem. The earlier it is detected, the lesser it is likely to get complicated.
Once a patient presents with either of the above complaints, doctor will perform a thorough examination of both the ears, irrespective to whether one or both ears have sustained damage. The doctor will also advise the patient to undergo an audiometry.
Who performs an Audiometry?
Audiometry is performed and interpreted by a qualified audiologist. Audiologists are doctors who have undergone training exclusively in hearing and speech problems, their diagnosis and treatment and rehabilitation.
How is Audiometry performed?
Audiometry is performed on out patient basis. There are no special preparations or precautions required for audiometry, except that the patient has to show up on time for the appointment. The following steps are involved in performing an audiometry:
-
The patient is asked to sit in a room which is sound proof. No external sounds can be heard inside.
-
Headphones are given to the patient.
-
Through the headphones, sounds of varied intensity and speed can be heard. An audiologist will monitor the whole process.
-
The patients will be asked to give some indication like raising their hand or notifying the doctor in some way when they are able to hear the sound.
-
Patients are also made to hear spoken words and are asked to convey the intensity at which they can hear the speech.
-
One type of audiometry test involves making the patient hear some spoken words with other sounds or noises in the background. The patient’s ability to distinguish the spoken words from the background noise is assessed and hearing loss is calculated.
-
Apart from this, the doctor may also place a vibrating tuning fork behind the ear and at the center of the forehead on top. A vibrating tuning fork may be brought near to each ear. Depending on the patient’s ability to hear the vibrations, the hearing loss can be assessed.
It is important to note that audiometry test is always performed on one ear at a time and never on both ears together.
What happens after Audiometry?
Depending on the intensity and speed of sound waves which the patient could hear, an audiologist or an ENT specialist will assess the presence, type and degree of hearing loss. If patients present with any hearing abnormalities, they are generally referred to an E.N.T specialist. Necessary treatment and rehabilitation is started and if required, the patient could be asked to undergo another audiometry for follow up.
Types of Deafness:
Audiometry helps to determine the site of damage. Following are two types of deafness:
-
Due to faulty bone conduction:
This type of deafness results from damage to the 3 bones; mallues, incus, stapes or to the bony cochlea. The bones cannot conduct sound waves forward appropriately, which results in diminished or complete loss of hearing.
-
Due to faulty nerve conduction:
Auditory nerve, vestibular nerve, cochlear nerve are the important nerves in the pathway of sound conduction. Damage to any of these nerves could occur due to infection, trauma or loud noise. This could lead to reduced or lost hearing.
Treatment of hearing loss:
Hearing loss can be permanent or temporary. Depending on the nature and cause of deafness, treatment can be initiated. It can be in the following ways:
-
Medicines:

Medicines-For-Ear
Medicines are useful to treat infections which are responsible for hearing loss. Bacteria, fungus or virus can be responsible for ear infections. If hearing loss is accompanied with pain, the doctor may also prescribe pain relief medicines to the patient.
-
Hearing aids:
Hearing-Aids
Devices which can be used externally or implanted within the ear can be utilized to enable better hearing. They modify the sound waves and help in transmission of proper signal to the area of brain which is responsible for normal hearing.
-
Ear muffs:

Earmuffs
It is advisable to get exposed to loud noises recurrently; more so in cases of reduced hearing. However, sometimes it is a professional hazard for some, to get exposed to loud noise all the time. Such people are advised to constantly use ear muffs to reduce the impact of harsh sound waves of the hearing apparatus.
-
Surgery:
In extreme cases, where damage to the ear is severe, medicines or allied therapy may not work alone. Surgery may be needed to repair the damage. Surgeries like ear drum repair surgery, cochlear implant, are necessary to return the hearing abilities back to normal.
A simple audiometry test can go a long way if done on time. It may seem insignificant, but it proves very useful in diagnosing and treating hearing loss. The above article sheds light on the necessity, technique and benefits of doing audiometry test. It will help the patient to know more about the process and its usefulness.