Swine flu aka H1N1 influenza 09, human swine influenza, or influenza A (H1N1) virus is an extremely communicable respiratory infectious disease and recent medical fear in India witnessing the death toll of 833 people till date. The name comes from the virus’ strain found in pigs which was accompanied by a new strain identified in 2009 that infected humans too.
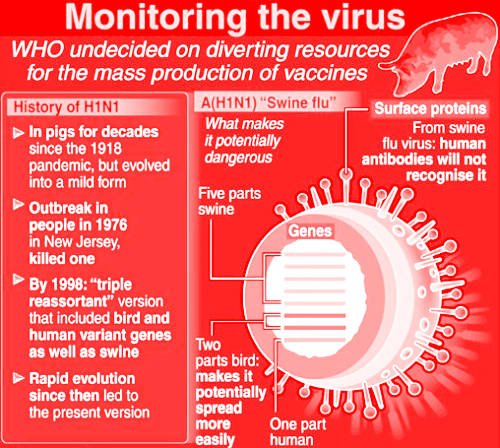
Due to its fast spreading nature around the globe, World Health Organization (WHO) called the virus as ‘pandemic’. The latest swine flu virus detected is H3N2 which was preceded by H3N2v in 2011 and the first ever H1N1 in 2009.
What are the symptoms?
- Sore throat
- Cough
- Nasal secretions
- Runny or stuffy nose
- Occasional vomiting
- Fatigue
- Rash
- High fever (≥100 F)
- Diarrhea (rare)
- Body aches
- Chills
Note that the symptoms of swine flu are similar to those a regular seasonal influenza or flu. Children are usually on high radar when it comes to H1N1 infection; they could be contagious as long as 10 days after getting sick. The infection in adults, on the other hand, could be communicable 7 days after they get sick and as early as 1 day before they show any symptoms. The symptoms are generally visible for about 1-2 weeks, whereas they could last longer in patients with a serious degree of the infection. Talking about the incubation period, with a mediocre period of 2 days, it is usually 1-4 days approximately from exposure to the first signs of the infection.
What about pH1N1 and its further complications?
Of all the different types of influenza, strain pH1N1 is the one you need to be extremely cautious about if you are suffering from a chronic condition including heart disorder or even obesity. Human swine flu, just as seasonal flu, can also worsen underlying medical conditions and other conditions like asthma, bronchitis, and diabetes. It is required of you to call your doctor right away if you develop signs like confusion, shortness of breath, dizziness, stomach ache, or extreme vomiting because swine flu could lead to some severe medical complications such as:
- Respiratory failure
- Pneumonia
- Sinus
- Ear infection
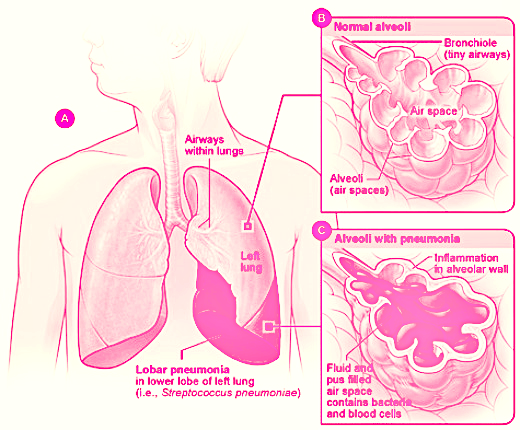
A form of lung infection, pneumonia is the most serious complication found in patients affected with severe H1N1 infection. Some of the frequently observed signs of pneumonia are:
- Cyanosis or appearance of blue skin around the mouth region due to lack of sufficient oxygen
- Breathing problems
- High temperature
- Cough
- Rapid breathing
- Abdominal pain
- Chest pain
- Feeling unwell and tired
- Headache
- Decreased appetite
The chances of your health getting deteriorated are more if you are chronically affected and infected by any type of flu for that matter, especially H1N1. You would probably suffer more with swine flu if you have a chronic problem as compared to anyone without it.
Patients with these conditions are exposed to a high risk of contracting severe swine flu:
- Liver disorder
- Chronic lung disease
- Heart disease
- Weakened immune system
- Kidney disorder
- Blood disease
- Central nervous system or any brain disorder
Should I eat pork products?
Although it first affected people like pork processors and farmers who were closely associated with pigs, swine flu cannot be contracted due to consumption of any pork products such as ham, bacon, etc. However, it is advisable to consume properly cooked and hygienically handled pork products for safety. Other than that, there is no major harm to eat pork meat. Even WHO says that swine influenza is non-transmissible among people who eat pork, even among those residing in countries where there had been a significant outbreak of the flu in the recent past.
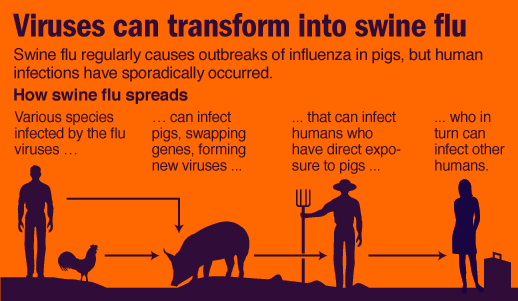
Then, how is human swine flu spread?
People (eg., pig farmers) dealing with pigs on a daily basis could more likely be infected with H1N1 virus, as they are required to handle sick pigs and sometimes are ignorant of the basic hygienic practices such as sanitizing hands, etc. In some cases, as studied, it is observed that the flu could be asymptomatic, as in the patient shows no symptoms and feels well; however, he yet could be infecting the people around.
The contagious human swine flu is spread in the same manner as the seasonal influenza through direct and indirect contact:
Direct contact –
While caring an infected person, if you mistakenly come in contact with his sneeze or cough droplets, you may catch the virus (sprayed in the form of miniscule drops in the air while sneezing or coughing).
Indirect contact –
If you happen to touch a contaminated article/object such as tissue, sanitary pad, etc., or any object for that matter such as washbasin or doorknob that an infected person has come in contact with recently then you are likely to catch the virus too.
Should I see my physician?
You are recommended to consult your physician immediately if your body begins to show flu-like signs. You would primarily be diagnosed via a throat or nose sample followed by physical examination and study of your travel and medical history.
It is also important to avoid taking swine flu medications unnecessarily as they may cause side effects and allergic reactions if you are not in close contact with infected individuals or diagnosed with H1N1 flu. Your doctor should direct you appropriately whether or not you really need to take the medications.
Are there any drugs to treat H1N1 flu?
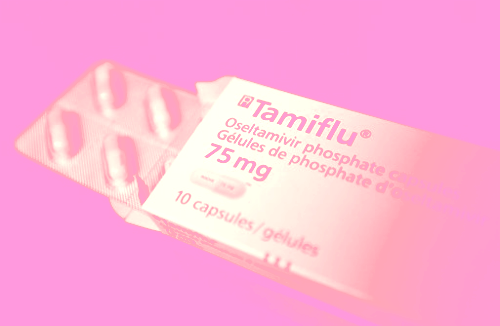
There are no dedicated drugs to treat the infection; however, these 2 are studied to work best against it if taken within 48 hours of detection of the first symptoms:
- Zanamivir (Relenza)
- Oseltamivir (Tamiflu)
Related symptoms like fever, pains, and aches could be treated with the help of over-the-counter drugs. But, make sure that children less than 18 years are not administered with aspirin to avoid the risk of Reye’s syndrome. Newly 2014 FDA approved drug peramivir injection (Rapivab) is a tested anti-influenza for H1N1 and other flu viruses.
Know that antivirals are most effective against H1N1 and not antibiotics because it is not bacteria.
Can vaccinations help?
Vaccines help to “teach” the body’s immune system to fight against the virus. The newly prepared intradermal (trivalent) vaccine is approved for people aging 18-64 years. The first (2009) H1N1 vaccine was in the form of nasal spray while an injectable type came later after 6 months.
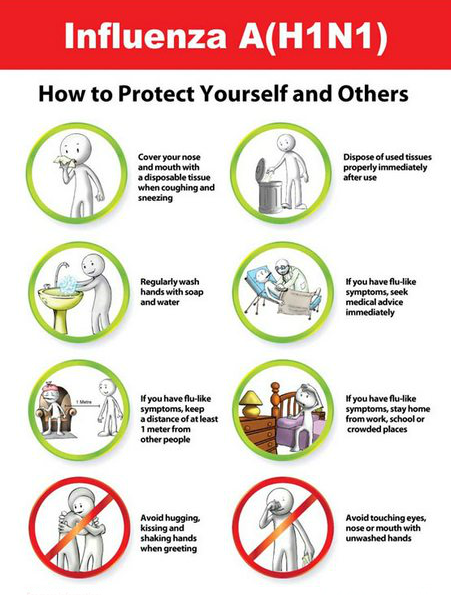
How to get protected from H1N1?
- Get enough sleep, drink plenty of fluids, avoid eating roadside/fast foods, and exercise daily
- Use a sanitizer whenever possible. Wash your hands and legs before eating food or preparing it, before and after treating wounds, changing sanitary pads, caring a sick person, after sneezing, coughing, and blowing your nose, and after using the washroom
- Avoid staying near sick people and in crowded places
- Avoid touching your nose, mouth, or face without sanitizing your hands