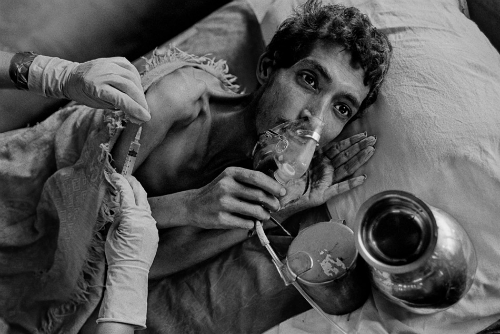
Tuberculosis (TB) is mostly detected in the lungs, which is called pulmonary TB. The gradually developing bacteria causing the infection are studied to thrive in areas where oxygen and blood are in abundance. However, the infection could spread to other areas as well. While the treatment could last from 6 to 9 months, there have been cases where patients had to undertake a 2 year long treatment.
What symptoms does a tuberculosis infected person reveal?
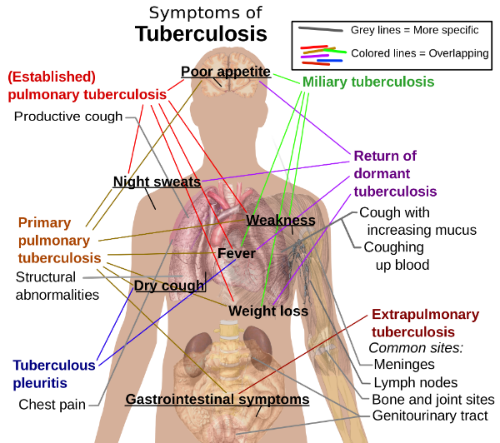
As a common case, symptoms of tuberculosis are confused with those of other similar conditions such as pneumonia, bronchitis, and lung cancer. Therefore, it is vital that you get yourself diagnosed through a doctor before committing to any treatment. The development of symptoms is usually very gradual and sometimes, the infected person is totally unaware about the infectious condition. At times, it may even take weeks to reveal the first symptoms.
Since the infection could make any part of the body its habitation, symptoms vary widely according to the infected part. For instance, neck pain could be a sign of swollen lymph nodes in the neck due to the infection whereas intense back pain could point out spinal tuberculosis.
Symptoms usually vary from no symptoms to active symptoms in cases of latent tuberculosis and active tuberculosis respectively.
- Night sweats
- Feeling unwell all along
- Feverish
- Fatigue
- Unexplained weight loss
- Heavy coughing with bloody or thick mucus
- Chills
- Chest pain
- Shortness of breath
You are advised to immediately consult your local doctor if you show signs of active tuberculosis or have been exposed to an actively infected person.
How can tuberculosis be spread?
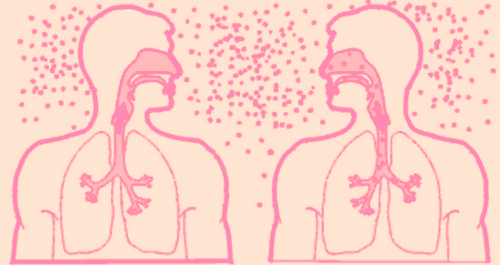
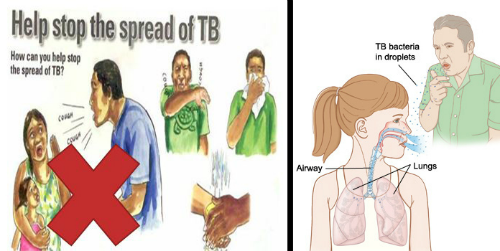
Talking, laughing, spitting, sneezing, and coughing by an actively infected person could spread the infection through air to another person. ‘Mycobacterium tuberculosis’ is the bacteria that cause the disease. The bacteria get settled in lung passages and air sacs once the person is infected. This highly contagious disease is not easily spread by an infected person if he has been undertaking proper treatment for approximately 2 weeks. The chances of catching the infection are more if you are in constant contact with the infected individual. For example, working in the same office cubicle or sharing a room with less ventilation.
Multi-drug resistant tuberculosis (MDR-TB) is a dangerous avatar of the disease which is developed when the bacteria become resistant to one particular antibiotic and often other multiple drugs at the same time. Having mentioned that, MDR-TB is curable and can only be treated using specific anti-TB drugs. Disappointingly, these drugs are not readily available.
Which factors could increase the odds of getting infected?
It should be noted that only those with active TB infection in their body could spread the disease. Here are some factors that could increase the chances of getting infected:
- Having frequent or close contact with untreated active TB sufferers. This is especially true for healthcare professionals who care for TB patients on a regular basis
- Having substance use problems
- Being addicted to smoking, tobacco chewing, drugs, etc.
- Having debilitated immune systems due to HIV/AIDS, poorly controlled diabetes, recent pregnancy, old age, new birth, and specific cancers
- Celiac disease or chronic lung disease caused due to inhalation of tiny sand, dust, or silica particles
- Traveling to or returning from regions such as Africa, Eastern Europe, South America, Asia, etc. where active TB is common
- Being deprived of health care facilities due to poverty, migration, homelessness, etc.
- Living in over-crowded areas such as prison, homeless shelters, military barracks, or nursing homes
- Weighing 10% above or below appropriate body weight
- Taking particular medicines such as tumor necrosis factor-alpha antagonists or long-term corticosteroids
How is tuberculosis diagnosed?
Early detection is essential as a precautionary measure. People at risk are usually advised to go for health screening by public health officials.
Latent tuberculosis diagnosis:
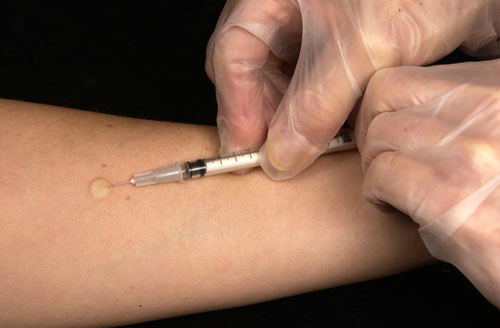
Interferon-gamma release assays (IGRAs) or rapid blood tests are used when tuberculin skin test does not provide clear results. People with BCG vaccination could also be diagnosed for TB infection using these tests.
Extra pulmonary tuberculosis diagnosis:
For diagnosing TB infection in other body parts leaving the lungs, more tests are involved. CT scan is mostly recommended when the infection has spread all over the body (miliary TB) whereas MRI scan is suggested for spinal TB or TB in the brain. Lumbar puncture is ordered by collecting some fluid around the spinal region to diagnose TB meningitis. Biopsy and urine culture are other tests that are ordered to diagnose specific TB types.
Active tuberculosis diagnosis:
Requiring at least 1-8 weeks for providing satisfactory results, sputum culture, where mucus from the lungs is tested, is recognized as one of the best tests to detect active TB. However, current symptoms, medical history, and physical examination are also considered when detecting the active infection. The doctor may also order sputum cytology test, if required. If you have an uncertain reaction to tuberculin skin test or a positive result to it or display active TB symptoms, you may be asked to perform a chest X-ray test.
How to avoid the infection?
According to WHO, a third of the world’s population is infected by the tuberculosis bacteria. While active TB is very contagious, it is vital that you consider these preventive measures to avoid the danger of getting infected:
- Having appropriate diet. Completing all your meals daily
- Using face masks if working in healthcare organizations
- Avoid staying in crowded areas or sharing rooms with large number of people and with no or less ventilation
- Encouraging your infected beloved ones whom you live with to undertake appropriate and complete treatment
How to care during treatment?
When caring for an infected person or for yourself while undertaking the treatment, it is essential to focus on taking the prescribed medicines on time and in the right measure. Besides, you need to report any side effects to your doctor as the medicines could be very strong and hard for your body to adjust to. You may lose weight quickly due to the infection; therefore, it is advised to eat high calorie and protein foods. Stomach problems are other effects which could be taken care of by drinking ginger or peppermint tea. Emotional issues are very commonly registered while undertaking the treatment. It is required of you to maintain your emotional state by seeking social help from a counselor or spiritual mentor.

I want to share the information with my friend. How can I do this?
Dear Pradip, thank you for showing your interest in MediFee. You can share this information through Facebook – https://www.facebook.com/medifee, Twitter – https://twitter.com/medifee_com, and by subscribing to our newsletter above (top right) – just enter your friend’s email address there. Or, you could simply share this link – http://www.medifee.com/blog/who-announced-india-as-the-highest-tuberculosis-burden-land/ with your friend via your mobile or by emailing.
Important information on tests, please visit – http://www.medifee.com.
Thank you! Keep reading!