Cardiac Catheterization
Listed below is the step by step procedure of cardiac catheterization:
- What is Cardiac Catheterization?
- Why is Cardiac Catheterization Required?
- Pre-operative Preparation
- Day Before Surgery
- Procedure Day
- Methods/Techniques of Cardiac Catheterization
- Post Procedure
- Risks and Complications
- FAQs
What is Cardiac Catheterization?
Cardiac catheterization is a diagnostic procedure employed by cardiologists to know the condition of heart health of a patient. It makes them decide whether further surgery is required. Since direct visualization of arteries supplying blood to heart is possible, various diseases of heart can be detected through this procedure. Arterial blockages due to deposition of plaque can also be spotted through this procedure.
Why is Cardiac Catheterization Required?
Cardiac catheterization is a very low-risk procedure. It is important for the doctor as it provides crucial information of the patient's health history. Cardiac catheterization is done for following reasons:
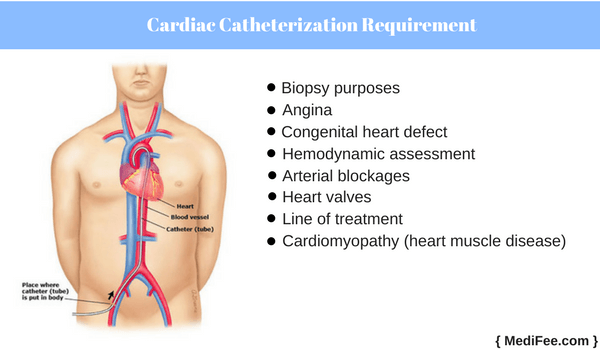
- Biopsy purposes: A biopsy can be combined with cardiac catheterization for extracting heart tissue for analysis.
- Congenital heart defect: Cardiac catheterization can identify probable congenital heart defect in a person.
- Angina: Through cardiac catheterization, blood vessels that are blocked and are causing pain can be identified. If the patient is suffering from shortness of breath and fatigue, causes of those can be investigated through cardiac catheterization.
- Hemodynamic assessment: Cardiac catheterization enables the doctor to assess quality of blood that is being supplied to the heart.
- Arterial blockages: Status of arterial (arteries that supply blood to the heart) blockages can be measured through cardiac catheterization. The exact location of the blockages and their severity is pinpointed through this test.
- Heart valves: A cardiac catheterization enables the cardiologist to look for disorders of heart valves and assess their functioning ability.
- Line of treatment: A cardiac catheterization helps the cardiologist in deciding the line of treatment for the patient if there is any significant problem detected through it.
- Cardiomyopathy (heart muscle disease): A cardiac catheterization identifies the condition that leads to enlargement of heart due to thickening of heart muscles.
Pre-operative Preparation
You are required to undergo blood tests for checking levels of hemoglobin, white blood cells, platelets, blood sugar. These levels should be normal in order to proceed further with the surgery. An electrocardiogram (ECG) once you get the day for cardiac catheterization scheduled.
Day Before Surgery
- Food consumption: The doctor will give you instructions about what to eat and drink during the day before the test.
- Medicines: You need to tell your doctor about any medicines you are on for any condition. The doctor might instruct you to go off them before the procedure. Do not discontinue the medication on your own.
- Fasting: There is the usual fasting for six to eight hours before the catheterization procedure.
- Allergic reaction: It is better to inform your doctor if you are allergic to rubber substances like latex or to medications such as penicillin. Also, let your doctor know if you show any negative reaction
- iodine and other such contrast agents.
- Medicines: You need to ask your doctor as to which medications you need to stop till the surgery gets over.
- Going home: Make arrangements for someone to drop you home after the test as naturally you won't be in a position to do so yourself.
- Hearing aid: Do not take off any hearing aids if you use, during procedure.
Procedure Day
On the procedure day, when you arrive at the hospital, following things happen before you are shifted to the operation theater for cardiac catheterization:
- Health history: The doctor makes a note of your health history.
- Intravenous catheter: The nurse connects a small intravenous catheter (IV) into a vein in your arm for administration of medications or fluids.
- Catheterization laboratory: You will be moved to the catheterization laboratory that has an X-ray camera for imaging purposes during procedure.
- Shaving: The groin or arm from where the blood vessel will be accessed is shaved and scrubbed with an antiseptic.
- Sterilized sheets: Sterilized sheets will be used to cover you.
- Sedatives: Sedatives will be injected to make you drowsy.
- Pregnancy: Inform the doctor about impending pregnancy as the procedure could hurt the fetus in the womb.
Methods/Techniques of Cardiac Catheterization
As mentioned before, a sedative will be delivered to you before the catheterization procedure begins. Heartbeat is continuously monitored through electrodes that are attached to your chest. The person does not feel a thing when the skin is numbed. A needle is inserted in the artery in arms or legs with the help of a guide wire. After this, an introducer tube is used to pass the catheter through guide wire. X-ray imaging is simultaneously done and catheter is removed. Removing blood tissue samples through catheter is also possible. During catheterization, the cardiologist can also use the catheter by placing its tip into different regions in the heart to measure the pressures within the heart chambers or for taking blood samples to measure oxygen levels.
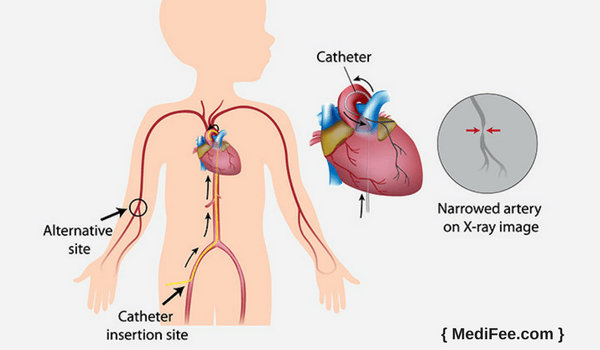
The catheter insertion site may be closed with a suture or a “plug†made of material that works with your body to create a natural clot in the artery. After that, either coronary angioplasty or thrombectomy is done if need is found or the person is shifted to the recovery area. Overnight stay in hospital is required if any other aforementioned procedure is performed.
Post Procedure
Once the procedure is over, you will be shifted to a recovery room. You will stay there until the effect of sedative wears off.
Rest, following the procedure, is very essential for proper healing of the operated blood vessel. Since it is an outpatient procedure, you are likely to return home the same day.
Do's and Don'ts Post Cardiac Catheterization
Following listed are the recovery tips to be followed in the period post undergoing cardiac catheterization:
- Avoid pressure: Avoid exercising pressure during bowel movements; at least for the first 3 to 4 days after the procedure, to prevent blood oozing out from the site of catheter insertion.
- Heavy objects: Avoid, pushing, pulling and lifting objects that weigh more than 10 pounds for the first week post procedure.
- Avoid sports: Strictly avoid participating in strenuous activities and contact sports for 5 days after the procedure. This includes most sports - jogging, golfing, play tennis, and bowling.
- Do not rush on stairs: Climbing and alighting stairs is fine, but avoid rushing up and down the stairs like kids.
- Baths: Do not take bath in a tub. Also, avoid swimming and jacuzzi for at least a week following the procedure.
- Gradually increase your activities until you reach your normal activity level within one week after the procedure.
- Dressing: The morning after your procedure, you may take the dressing off. The easiest way to do this is when you are showering, get the tape and dressing wet and remove it.
- Cover site: After the bandage is removed, cover the area with a small adhesive bandage. It is normal for the catheter insertion site to be black and blue for a couple of days. The site may also be slightly swollen and pink, and there may be a small lump (about the size of a quarter) at the site.
- Washing site: Wash the catheter insertion site at least once daily with soap and water. Place soapy water on your hand or washcloth and gently wash the insertion site; do not rub.
- Catheter insertion area: Keep the catheter insertion area clean and dry when you are not showering.
- Avoid usage of cosmetic products: Do not use cosmetic products like creams, lotions or ointment on the wound site.
- Wear loose clothes: Prefer loose and comfortable clothing.
Risks And Complications
There are very few complications associated with cardiac catheterization which are as listed below:
- Bruises: Some people develop bruises at the site of catheter insertion.
- Blood vessel damage: In very rare cases, cardiac catheterization may cause damage to nearby blood vessels during the procedure.
- Irregular heartbeats: The person may experience an irregular heart rate. But this condition goes away on its own and is no reason of concern.
- Cardiac tamponade: Sometimes a fluid build up or that of blood in the sac that surrounds the heart takes place post catheterization. Such a fluid can change patterns of heartbeats.
- Blood clots: Heart attack or stroke triggered because of blood clots is another risk.
- Groin bleeds: Groin bleeds are a common cause of mortality associated with cardiac catheterization.
FAQs
- What are the benefits of cardiac catheterization?
A. Cardiac catheterization helps the doctor detect any bigger problems of heart and conduct corrective surgery on time
- Will I be asleep during the procedure?
A. No, if any interventional procedure is to be done, the person is given anesthetic for making them unconscious.
- How long does it take to do a cardiac catheterization?
A. The procedure lasts anywhere between 30-45 minutes. The procedure will last longer if any other cardiac procedure is decided to be done.
Related Information
List of best Cardiologists in India and top cities
List of best Cardiology Hospitals in India and top cities

