A tumor in the brain is a mass of some abnormal cells. This mass can be malignant or benign. Malignant tumors are cancerous and benign tumors are non-cancerous. Primary brain tumors originate in the brain; these form in the brain tissues. Secondary brain tumors originate in other parts of the body and spread to the brain. Usually malignant tumors become secondary tumors which form when cancer spreads from other parts of the body. 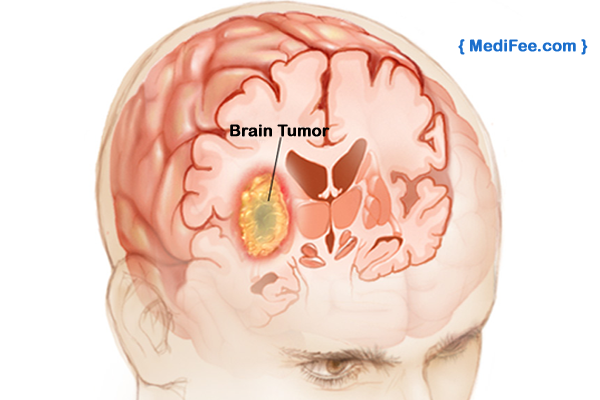
Symptoms and Diagnosis:
The symptoms of brain tumor are seizures, vomiting, headaches, nausea, issues related to vision or hearing, etc. These are the usual symptoms. However there are certain symptoms that are specific to the location of the tumor: pressure near the location of the tumor, problems in performing motor activities, inability to look upward, changes in the emotional state, changes in the perception of pressure or touch, confusion regarding right and left sides of the body etc. 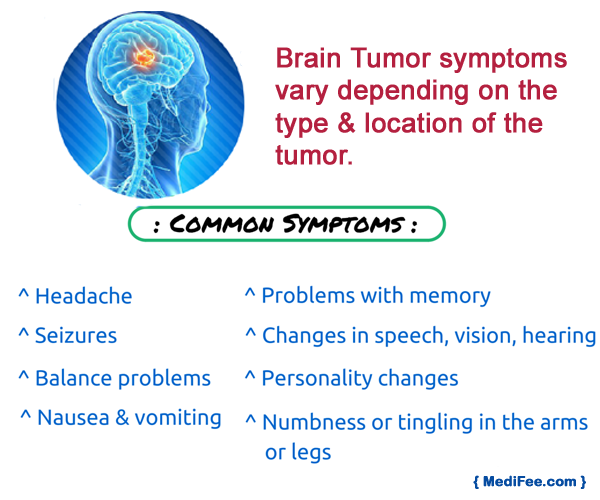
When a person has one or more of the above mentioned symptoms, their doctor will do some tests, besides checking the general health signs. The following tests are usually required for the diagnosis of brain tumor:
-
Neurologic Exam:
During this exam the doctor will examine the patient’s eyes to check if there is a swelling resulting from a
tumor’s pressure on the nerve connecting the brain and the eye. The doctor will also study the type of response to pain, if any. -
Computed Tomography (CT) scan:
To know the existence of tumors in the brain, CT scans are used. The patient may be injected witha special dye that will help getting clear pictures of the inside of the brain.
-
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI):
Unlike CT scan, MRI uses magnetic field and radio waves to take detailed pictures of the brain.
 The radiologist may inject a special dye into the bloodstream to show the differences between healthy tissues and abnormal tissues.
The radiologist may inject a special dye into the bloodstream to show the differences between healthy tissues and abnormal tissues. -
Angiogram:
This is another popular test for diagnosing brain tumors. During this test a special dye is injected into the patient’s
arteries in the brain. This dye helps the doctor to clearly see the blood vessels on an x-ray. Through this test, the doctor will be
able to detect the presence of a tumor in the brain. -
Spinal Tap:
Spinal tap is also known as lumbar puncture. It is used to find out cancer cells in the cerebrospinal fluid, the liquid that surrounds the spinal cord and brain. During this process, the patient will be injected for local anaesthesia in the lower part of the back near the spinal cord. Then the doctor inserts a small, hollow needle between the bones of the spine to remove some fluid from the spinal column.
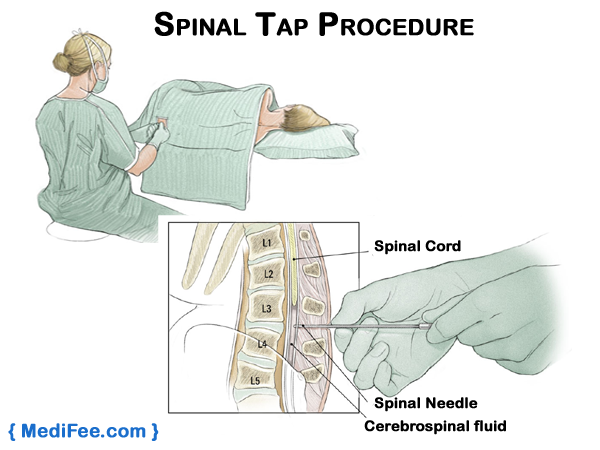 This fluid is tested under a microscope to look for cancer cells. Although this test is considered safe, but doctors need to take extra care while withdrawing the fluid so that the pressure in the fluid does not drop largely, which could give rise to serious health issues. Spinal tap is mainly done to look for a tumor that has chances to spread commonly through cerebrospinal fluid.
This fluid is tested under a microscope to look for cancer cells. Although this test is considered safe, but doctors need to take extra care while withdrawing the fluid so that the pressure in the fluid does not drop largely, which could give rise to serious health issues. Spinal tap is mainly done to look for a tumor that has chances to spread commonly through cerebrospinal fluid. -
Myelogram:
- This test allows the doctor to detect a tumor in the spinal cord. During this test, a special dye also known as contrast
material is put into the subarachnoid space (fluid-filled space) with a needle and the patient is tilted so that the dye mixes with the
fluid. After that, x-rays are used to take pictures of nerve roots and spinal cord. -
Skull X-ray:
- The doctor uses skull x-ray to learn about any calcium deposit in the brain. Many times changes in the skull bones are also checked using the X-ray.
-
Biopsy:
o Surgical Biopsy: This biopsy is done during the tumor removal surgery. The surgeon will take a hard-to-reach tissue sample during
the surgery.
o Stereotactic Biopsy: During this process, either CT or MRI is used. The images captured by these devices help the surgeon to determine the exact location of the needle in the targeted tissue from the tumor.
o Needle Biopsy: Like other needle biopsies, the surgeon uses a needle to remove the suspicious tissue sample. But a small hole in
the skull is first made, known as blur hole in order to pass the needle through it.
Risks Associated with Screening:
Although the tests are the only ways to detect brain tumors, sometimes these tests may pose some risks. For example, during a stereotactic
biopsy there are chances of bleeding which can cause mild problems like headache to serious issues like stroke, coma and the worst, death.
The risk of mortality is 1%, whereas the risk of bleeding after the biopsy is 5%.
During MRI, CT scan or angiogram, some people may react to the contrast material and have issues like rash, wheezing, itching or facial
swelling, pain at the needle site, nausea, low blood pressure and headache that develops sometime after the test gets over.
Cost:
The costs for brain tumor testing vary in different cities and depend definitely on the standard of the hospital, you are choosing to get your treatment from. You can find the list of cities that offer MRI scan with their respective prices here. Before selecting the hospital, you must learn about the doctor and their experience, so that you get the best treatment even when you have to spend a hefty amount of money.