Lumbar Puncture
Listed below is the step by step procedure of lumbar puncture:
- What is Lumbar Puncture?
- Why is Lumbar Puncture Required?
- Pre-operative Preparation
- Day Before Surgery
- Procedure Day
- Methods/Techniques of Lumbar Puncture
- Post Procedure
- Risks and Complications
What is Lumbar Puncture?
Lumbar puncture is a method of collecting cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) by inserting a needle between the 1st and 2nd lumbar vertebrae. Cerebrospinal fluid surrounds brain and spinal cord and acts as a buffer against traumatic impact.
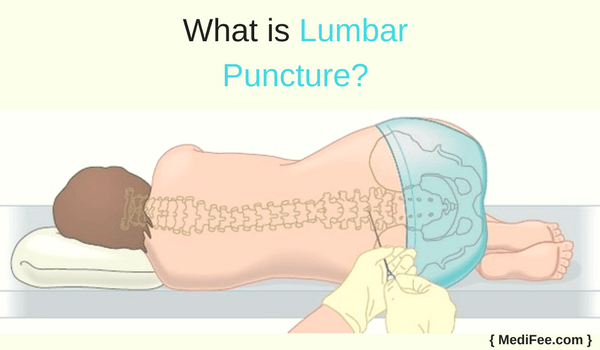
Lumbar vertebrae form part of the vertebral column, corresponding to the lower back. They are five in number. Lumbar puncture is performed by inserting a needle between either of the first two lumbar vertebrae and withdrawing CSF. The brain is surrounded by 3 protective layers. These layers extend into the vertebral column to surround the spinal cord as well. Two of these 3 layers have to be punctured to obtain the cerebrospinal fluid. Hence the procedure is known as lumbar puncture. It is also known as spinal tap.
Why is Lumbar Puncture Required?
Lumbar puncture is often employed as a diagnostic procedure for detecting cause of some disorders related to the brain. It also has therapeutic uses in some cases. Some indications that lumbar puncture is needed are mentioned below:
- Examination of CSF
CSF collected by lumbar puncture is subjected to pathological examination. Cancer of brain, presence of infection, inflammation, can be detected after microscopic examination of CSF. Presence of RBCs in absence of evidence of bleeding within the brain can be detected. Health conditions like meningitis, multiple sclerosis, intracranial hemorrhage, Guillian Barre syndrome, can be detected by CSF examination.
- CSF culture
If there is suspicion of brain infection, CSF obtained after spinal tap is cultured. This means, it is treated with suitable chemicals or gels and placed under suitable environmental conditions. This will help to detect presence of any infectious bacteria.
- Non-microscopic Examination
Sometimes, there is no need to perform a microscopic examination of CSF. Its appearance can be abnormal at times and is enough to provide a basic idea about what the patient could be suffering from. Healthy CSF is a colorless liquid. Sometimes it may be mixed with blood which could be an indication of brain trauma. In case of infection or cancer, cerebrospinal fluid appears turbid.
- Measuring Intracranial Pressure
Due to presence of CSF a certain pressure is maintained around the brain and spinal cord. This pressure can be measured during lumbar puncture. It is measured by attaching a manometer to the needle which is inserted into the vertebral column. Elevated pressure is a sign of some underlying abnormality. Further examination of CSF will provide an appropriate diagnosis.
- Relieving Elevated Intracranial Pressure
At times, intracranial pressure is elevate, which may lead to symptoms. To alleviate the pressure and provide symptomatic relief, lumbar puncture is often done to drain some CSF. This normalizes the intracranial pressure for the time being. The exact cause of the condition has to be diagnosed and treatment needs to be initiated promptly to avoid complications. This will be helpful only if there is no lesion in the brain. Increased pressure due to brain lesion will not be relieved with lumbar puncture.
- During Other Investigations
Lumbar puncture may be done prior to CT scan of brain or performing a myelogram to inject dye. This helps in visualizing brain and spinal cord during the procedure.
- For spinal or epidural anesthesia: Spinal canal can be performed to administer regional anesthesia prior to surgery. By performing spinal tap, anesthetic medicines can be administered into the spinal cord or into the epidural space. Spinal or epidural anesthesia is beneficial as the patient remains conscious and sensation over only the lower body is temporarily lost.
- To administer medicines: Medicines can be administered into the spinal canal by performing a lumbar puncture. If introduced directly into the spinal canal, they reach the nerves faster and act more rapidly. Chemotherapeutic medicines are often administered through lumbar puncture needle.
- Emergency lumbar puncture: Emergency lumbar puncture could be employed in cases of a pre-existing brain disorder to provide symptomatic relief from elevated pressure on the brain. Draining the CSF will provide temporary relief to the patient. This has been explained above in detail.
Pre-operative Preparations
Lumbar puncture is not an operation. It is a procedure performed on out patient basis for therapeutic or diagnostic purpose. Following, are some of the pre-requisites of lumbar surgery:
- Discussion with the patient: The doctor who will perform lumbar puncture, will explain the procedure to the patient, along with its pros and cons. Patient may be asked to provide with a written and signed consent which states that they are willing to undergo the procedure.
- Medicines: Patients undergoing lumbar puncture should provide their doctor with a list of other medicines they might be taking for any health condition. Medicines like blood thinners might be stopped for some days prior to surgery.
The surgeon will usually inquire about any allergies the patient might be having. Sometimes, patients might be allergic to a particular anesthetic agent. The surgeon will then avoid using it during lumbar puncture.
- Investigations: Prior to lumbar puncture, the patient be asked to undergo an MRI or CT Scan of the brain and spinal cord. It helps to observe any abnormalities in the spinal cord or brain. Any change in the alignment of the spinal cord, presence of spinal tumor or any other spinal pathological changes can be visualized. These are helpful in determining the course of lumbar puncture. Some pathological changes contraindicate lumbar puncture.
- Other Health Conditions: The patient must inform their surgeon about any other health condition they might be suffering from. Additional care and treatment might be needed for patients who have history of bleeding disorders. Women who are pregnant or might be pregnant should inform the surgeon about it.
- Assembling a Team: A qualified neurosurgeon who has good surgical skill and precision will head the team of medical professionals who will be responsible for successful completion of the lumbar puncture. A pathologist may also be on board. They will perform a microscopic examination and culture of the CSF obtained after lumbar puncture. Well trained and skilled nurses are an integral part of the team as well.
Day before Surgery
The day before lumbar puncture, patient is advised to rest and remain at home. They should prepare for the next day in advance. Lumbar puncture does not require to remain hospitalized after the procedure is over. But the patient will require to rest even after returning home. They should arrange for someone to accompany them to the hospital or medical center. They should arrange some help at home as they will not be able to perform strenuous activities for a day or two after the procedure. Undue physical exertion is to be avoided. The patient should remain mentally relaxed and avoid any stress.
Procedure Day
On the day of lumbar puncture, patient is expected to reach the hospital well in advance before the scheduled time of the procedure. They will be asked to get changed into a loose fitting, sterilized surgical gown. The procedure can be performed in an operation theater or in a clinic set up. The patient will be asked to lie down on the side with neck bent forward and knees bent and held close to the chest. This will stretch the vertebral column and provide more space between the vertebrae for the surgeon to access during lumbar puncture. The position of first and second vertebrae is determined and skin over them is cleaned with an antiseptic solution. Local anesthesia is used to desensitize this part of skin, so the patient does not feel any pain when the lumbar puncture needle is inserted.
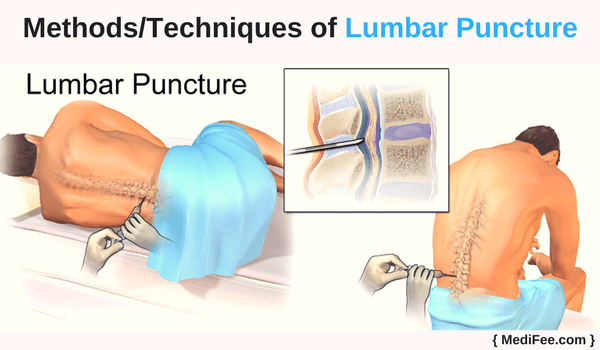
Methods/Techniques of Lumbar Puncture
Following are the steps involved in a lumbar puncture:
- Once the local anesthetic desensitizes the skin over lower back, lumbar puncture procedure is started. A long hollow needle is inserted into the space between two adjacent lumbar vertebrae. It will puncture the protective layer covering the spinal cord and pass further, till CSF can be aspirated.
- As the puncture is being performed there could be momentary pain or discomfort which passes away instantly. After the puncture is successful, the patient might be asked to relax their position a little bit. The neck can be returned to neutral position.
- CSF pressure is measured before and after withdrawing a small amount of the fluid. The needle is removed and the site is dressed with surgical bandage.
- The entire procedure is performed under fluoroscopic or CT guidance. Extreme precaution has to be taken to avoid damage to spinal cord. It can lead to permanent damage of some body functions corresponding to the area of damage.
Post Procedure
Before being discharged to go home, the patient is provided with a list of dos and don'ts which they are expected to follow. They are also given post-procedure instructions which will reduce the chances of complications after lumbar puncture. Some of these instructions are mentioned below:
- Physical Activity
The patient is advised to take adequate rest for a few days after lumbar puncture. It is advisable to avoid physical exertion. Back muscles should not be over strained. However, complete absence of activity is also equally harmful. It is advisable to move around, do light work, take short walks. It is essential to remain ambient as this promotes blood circulation and faster healing.
- Medication
After lumbar puncture, pain killer medicines are prescribed. They will help to combat pain which may be felt in the back at the site of puncture. Depending on the diagnosis made after CSF examination, other medicines can be started to treat the existing brain condition.
Risks and Complications
A few risks are associated with lumbar puncture procedure. They can be treated with medicines or other treatment methods. Some of the common risk factors are mentioned below:
- Headache: Some patients might experience headaches for 1-2 days after lumbar puncture. They are advised to take pain killers for the same. While sleeping, it is advisable to keep the head slightly elevated above the feet. This can be done by using pillows or blankets beneath the head.
- CSF Leak: If the surgeon performs the puncture incorrectly, some CSF may leak out of the spinal canal. The defect via which leak occurs can be sealed by applying a patch of the patient's own blood at the site.
- Bleeding: Bleeding could occur at the site of lumbar puncture. It has to be cleaned and the skin covered with soft cotton and gauze to prevent further bleeding.
- Accidental Damage to Spinal Cord: The spinal cord or nerves arising from it could suffer from trauma due to improper insertion of lumbar puncture needle. Patient might develop symptoms depending o the intensity of damage and site of damage. A neurologist must be consulted with immediately for further treatment. Physiotherapy might helps such patients.
More information related to Spine Surgery
- Information on Spine Surgery
- Information on Spinal Fusion Surgery
- Information on Spinal Decompression Surgery
- Information on Laser Spine Surgery
- Information on Cervical Spine Surgery
- Information on Laminectomy
- Information on Lumbar Discectomy
- Information on Vertebroplasty
Cost of Spine Surgery in India and top cities
List of best Spine Surgeons in India and top cities
List of best Orthopedic Hospitals in India and top cities

