While that sip of water had always been regarded as a life savior; today, we are afraid that it can even turn a menace to our own health. Indians are already having a tough time dealing with existing water crisis problems. Moreover, to work out a solution for this plight, is it enough to just have a continuous supply of water? The answer is NO. It is not about the availability of water alone, but safe drinking water is what we need to strive for.
Water borne diseases are the leading cause of death in India. And still we have thousands who consider “clear looking water” to be clean or safe, and thus use it for drinking purposes!
A glass of water that appears to be clear, is not always uncontaminated and safe to drink. Water borne diseases are related to microbes and definitely these are not visible with naked eyes. And who knows, water that looks clear may in real have millions of germs that can get you seriously ill.
There are a number of fatal diseases related to water. Understanding these diseases, finding their root causes, and more importantly, knowing how we can prevent the same, is the only possible means of keeping this life saving natural resource from jeopardizing our own health and life.
When does water become a source of water borne diseases?
Presence of pathogens in the water we use, gives rise to water borne diseases. Microorganisms of any type (bacterial, virus, protozoans, parasites etc.) can equally prove detrimental to our health; giving rise to multiple water related illnesses.
Although water borne illnesses are considered to be caused only by drinking contaminated water; you need to know that it can also arise by coming in contact with polluted water while bathing or washing. Intake of food cooked with contaminated water can also lead to serious health disorders.
Can water borne diseases spread from person to person?
Water borne diseases do not pass from one person to another; unless very poor sanitary habits are followed. The disease is considered infectious, as fecal matter containing germs finds its way into water sources easily due to poor maintenance. Thus, when this infected water is used by humans, they get affected with any of the different types of water borne diseases.
Top 6 water borne diseases in India:
Below listed are the top 6 water borne diseases in India:
- Cholera
- Typhoid Fever
- Hepatitis A
- Malaria
- Dengue Fever
- Shigellosis or Bacillary Dysentery
Cholera:
An infection of the small intestine caused by a bacterium named Vibrio Cholerae. Bacteria when enters the body, releases a toxic substance that inflames the small intestine. Thus, the organ fails to reabsorb excess water and this results in severe watery diarrhea that ultimately leads to dehydration and may prove fatal.
Causes:
- Drinking water supplies that are polluted with fecal matter containing cholera germs
- Vegetables that are nurtured with polluted water containing animal or human feces with germs
- Food cooked under unhealthy conditions
- Uncooked sea food
Symptoms:
Cholera symptoms are experienced within a few days post infection. However, sometimes the symptoms can also appear just after a couple of hours of bacterial infestation. Following are common symptoms of Cholera:
Symptoms include:
- Watery diarrhea
- Severe vomiting
- Dehydration
- Dry mouth due to excessive loss of water
- Muscle cramps due to loss of minerals from body during dehydration
- Fatigue and Drowsiness
- Less urination
- Irregular heart beat
Diagnosis:
If you are experiencing the above mentioned symptoms, visit your doctor immediately to facilitate early detection and treatment. Cholera can be easily detected using the following methods:
- Assessment of symptoms
- Stool Culture Test: Stool samples are collected and tested under laboratory conditions to detect presence of Vibrio Cholerae
- Blood test: Conducted only to detect antibodies generated for fighting back cholera germs
Treatment:
- Controlling dehydration is the first step. As cholera leads to excess loss of water and minerals from body, taking ORS to combat this condition is essential.
- Antibiotics to reduce the frequency of diarrhea is also administered
- Intravenous hydration can also be adopted under severe situations
Prevention:
A lot can be done on our part to prevent cholera. Some of the effective measures have been mentioned below:
- Boiling water for around 3 minutes before use is suggested
- Disinfecting water using chemicals
- Using treated water for washing vegetables and fruits before eating
- Avoiding under cooked food; especially, sea food
- Abstaining from street food
- Not using ice in drinks
- Careful disposal of fecal matter, cloth or anything containing blood stains; precisely those from infected patients
- Proper sewage disposals
- People who are traveling can partially benefit from cholera vaccines
Typhoid Fever
Typhoid fever relates to Salmonella Typhi, a bacterium that enters the human body and thus causes the disease. The bacterium slowly multiples within the bloodstream and finally is absorbed by digestive or gastrointestinal tract. As bacteria infest the digestive tract, related symptoms and discomforts are experienced. Severe typhoid fever may lead to internal bleeding.
Causes:
- Drinking water containing germs
- Eating half cooked food infected with bacteria
- Poor sanitary habits
- Dry sewage is a primary source of salmonella bacteria
- Vegetables and fruits that had been exposed to water or soil containing germs become a source of typhoid fever
- Sexual activities with people suffering from bacterial infection

Symptoms:
- Very high fever accompanied with headache
- Severe stomach or abdominal pain
- Constipation in adults and diarrhea in children
- Reduced appetite
- Skin rashes on chest and stomach
- Muscle cramps
- Fatigue and loss of concentration
- Severe infection may lead to blood stains in stool
Diagnosis:
Determining typhoid fever depends on detecting the presence of Salmonella Typhi in blood, stool or urine. For this purpose, following three tests are recommended:
- Urine Culture test
- Blood Culture test
- Stool Culture test
Besides, a bone marrow culture test can also be conducted and is considered to be one of the most effective diagnosis methods. However, as it consumes a lot of time, this test is opted as a secondary option. Using a CBC test to identify antibodies developed against the bacterium is also beneficial.
Treatment:
Antibiotics are the most effective treatment options for typhoid fever. However, medication is only helpful when proper supportive care is also adopted. Eating healthy food in shorter intervals, drinking plenty of fluids, and taking rest are vital for early recovery.
In rarest of cases, gallbladder removal surgery may be required to eliminate any probability of future infection. Treatment with antibiotics may make people feel better within a week or two; however, completion of the entire course of medicine is essential to ensure long time benefit.
Prevention:
- Using boiled water for most of your daily needs
- Eating hot food is highly recommended
- Using ice made from water stored in bottle
- Avoiding junk food
- Frequent hand washing with soap; even when you do not use hands to eat is advisable
- Typhoid vaccinations are also helpful in preventing the disease
Hepatitis A:
Hepatitis A is an infection of liver caused by Hepatitis A virus, disrupting the normal functioning of the organ. Hepatitis A is not fatal at early stages. Rather, most infants and young adults do suffer from this common waterborne disease.
However, the disease shows no symptoms in few cases and it is then that the condition becomes life threatening. Again, elderly people suffering from hepatitis A need special attention as the disease in this stage may lead to further complications and death.
The virus can enter the body through contaminated water and/or food. However, the good news is, the disease can be well prevented with vaccinations.
Causes:
- Drinking water containing the virus
- Eating undercooked food especially meat and sea food
- Cooking food with contaminated water
- Being in close contact with people already suffering from the disease
Symptoms:
Hepatitis A shows symptoms only after four weeks after the virus has actually infested the body. In addition, there have been cases where the disease comes up with no visible symptoms for long duration. Following are some of the common symptoms of Hepatitis A:
- Fatigue and a general feeling of weakness
- Muscle pain and overall body aches
- High Fever
- Upper abdominal pain
- Yellowish discoloration of skin and eyes, commonly known as Jaundice
- Itchiness of skin
- Change in the appearance of urine and stool. Urine goes darker than usual and stool get pale.
Diagnosis:
A doctor can determine Hepatitis A by simply knowing your symptoms. Yellowish discoloration is the most vivid symptom that confirms hepatitis A. However, opting for a Hepatitis A test, stool and urine tests are advisable and very essential.
Treatment:
- Medications to reduce severity of symptoms are usually prescribed to patients suffering from Hepatitis A
- Antibiotics and mild painkillers are also suggested to reduce fever and joint pain
- Keeping yourself hydrated during the entire medication span is of utmost importance
- Eating small and light food are vital to speedup the healing process. Since the intake is small, frequent eating is essential
- Total abstain from alcohol and smoke is vital
Prevention:
- Patients suffering from the disease need to remain isolated for a few day as the disease is contagious. This prevents spreading the disease to family members or anybody who comes in contact.
- Washing hands before eating
- Avoiding food that are not prepared in a clean and hygienic manner
- Drinking only purified water
- Keeping your surrounding clean
- Finally, as already mentioned Hepatitis A can be well prevented with vaccinations
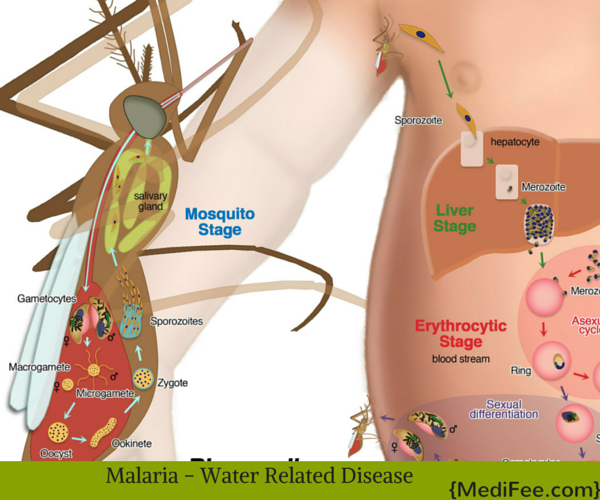
Malaria:
Malaria is a disease that leads to itsinfection spreading through the bloodstream and is caused by female anopheles mosquito bites. However, just after a mosquito bite, the infection spreads across liver and then hits the red blood cells. Now, the question is, how is malaria, caused by mosquito bites, a water borne disease?
As these infected mosquitoes breed in stagnant and dirty water, Malaria has been categorized as water borne disease; precisely after the Tsunami attack in India. Just after flooding, Malaria was found to infect a large number of people and hence, the disease was categorized as flood related and thus a water borne disease.
Causes:
Female anopheles mosquito is the only parasite that can infect people with malaria. These mosquitoes are abundantly present in stagnant water sources and contaminated water bodies.
Once the infection spreads into the blood stream, any uninfected mosquito that bites a person suffering from the disease becomes infected. Thus, now the mosquito is equally capable of causing the disease.
Symptoms:
Malaria shows no symptoms for around 7-15 days post infection. However, after a week or two, following symptoms are experienced. It must also be noted that malaria symptoms follow a fixed periodic repetition and lasts for around 6-8 hours initially.
- Cold and shivering
- Fever with severe headaches
- Sweating abnormally with disappearance of fever
- Extreme fatigue when not in fever
- Breathing problems
- Anemic symptoms
- Convulsions and muscle cramps
Diagnosis:
- A doctor will be able to determine malaria by knowing your symptoms
- However, a physical examination to know about your liver and spleen conditions is also conducted. An enlarged liver or spleen confirms malaria.
- Malaria Blood test is mandatory to learn about the infection
- Further, diagnosing for anemia is highly recommended to prevent future complications
- Patients suffering from severe malaria are also tested for signs of organ failure
Treatment:
Treating malaria early is crucial to stop this disease from turning fatal. Overnight stays in hospitals are the best way for administering quick treatments.
Antibiotics to reduce the severity of symptoms prove helpful. However, changes in medication are a part of the treatment and if your doctor is frequently changing doses, don’t get puzzled. Germs become resistant to doses after a while and therefore changing antibiotics becomes necessary.
Prevention:
Keeping your surrounding clean to avoid accumulation of stagnant water is the first step to take. Besides, using mosquito net and repellents is also suggested. However, repellents may sometimes lead to skin rashes in people. Therefore, talk to your doctor before opting for any repellent.
Dengue Fever:
Dengue fever can be caused by any of the four types of viruses known as flaviviruses. These viruses are transmitted by mosquitoes. And since mosquitoes breed in dirty water, dengue has been categorized as a water related disease.
An infected mosquito, biting a healthy person, leaves the poison within the bloodstream and thus causes a variety of symptoms. Being infected with one type of virus, makes a person immune to that particular pathogen for a life time. However, as there are three other types of viruses, that have not invaded the body yet, the person remains equally susceptible to dengue fever that can be caused by other viruses.
Dengue fever, also known as break bone fever, is very common with infants as well as adults. The disease may prove fatal if early treatment is not adopted.
Causes:
A mosquito biting a person infected with dengue acquires the virus for a life time. Therefore, when the mosquito bites other healthy individuals, it passes the same virus to them and thus they get infected with dengue fever.
Dirty stagnant water is the best thriving place for mosquitoes and black flies. Therefore, water accumulation needs to be avoided.
Symptoms:
- Excessive muscle and joint pain
- High fever and headache
- Skin rash that keeps appearing and disappearing
- A blunt pain behind the eyes
- Vomiting and nausea
Severe dengue known as Hemorrhagic fever may cause the following:
- Bleeding from gums, nose and mouth
- Internal bleeding leading to black stool and vomit
- A damage to blood vessels
- Fluctuating blood pressure
Diagnosis and Treatment:
Discussing symptoms with your doctor will help him/her to suspect dengue. In addition, the body rash that appear, are also an important indicator of the disease. However, a doctor will definitely order a blood test to confirm the presence of viruses causing disease. Dengue IgM and Dengue IgG are the two mandatory tests during dengue fever.
Based on your laboratory reports, your doctor will prescribe medicines that will definitely reduce severity of symptoms to a great extent. Spending a few nights in the hospital will prove beneficial as it facilitates continuous observation and thus quick treatment.
Keeping yourself hydrated during the course is one of your primary tasks while under treatment. Dengue, or for that matter any water borne disease, drives out a lot of fluid from your body; therefore, drinking plenty of water and healthy fluids in different forms is advisable.
Prevention:
Taking measures to keep yourself far from any probable chances of mosquito bites is the only effective step to be undertaken. For this purpose, you can use repellents, mosquito nets, or any other measure that can prove beneficial.
Besides, not allowing water accumulation nearby your living areas is another important step you need to take.
Shigellosis or Bacillary Dysentery:
A potentially dangerous bacterial infection affecting the colon lining. The disease is more common with children than adults. The disease largely affects individuals living in poor sanitary conditions, and therefore is a common health concern in developing countries. The bacterium attacking colon results in severe dysentery and related problems.
Causes:
- Although Shigella bacterium is the most common cause, E.Coli and parasitic amoeba can also lead to this disorder.
- Poor disposal of fecal matter containing germs serves as the biggest source of this dysentery.
- Flies thriving on fecal matter can transmit the germs easily. Thus, this disease is regarded as a highly contagious health ailment.
- Eating food or drinking water containing germs gives easy access to pathogens to invade your body and colon.
Symptoms:
- Loose stool accompanied with mucous and blood
- Lack of appetite
- Vomiting and nausea
- Stomach pain and cramps
- Some people may experience severe pain during bowel movements
- Dehydration and loss of weight
Diagnosis:
- Laboratory stool culture
- Colonoscopy may be adopted by some doctors
- A blood test is also conducted to know if any anaemic symptoms have developed
Treatment:
Antibiotics are prescribed to reduce severity. However, too much of antidiarrheal drugs may prove otherwise. Repeated bowel movement eliminates the germs from body. And therefore, this shouldn’t be restricted completely.
Eating very light food and plenty of water is important to help medicines do their work. Completely abstaining from food is not at all wise. In addition, as the disease is highly contagious, keeping patients slightly away from others in family will prevent its spread. Careful disposal of body waste, and personal hygiene is a must.
Prevention:
Avoiding unhealthy food or impure water is the best way to prevent the disease. Following proper sanitary habits is another important and effective measure to prevent the disease. If you are taking care of a patient suffering from this disease, make sure that you discuss your safety measures with the doctor before hand.
These were the most common water borne illnesses in India. Apart from all the above mentioned precautions specific to diseases, there is one more vital step that is to be taken by all of us. Educating people and ourselves about a healthy life style and measures to keep the environment or surroundings clean are two effective measures that can protect us from any water borne disease . Be responsible not only towards your own health, but your surroundings as well, is sufficient to prevent any microbial disease.