Pathology – a medical branch that aims at laboratory testing of body tissues and fluids to determine diseases; their causes, nature and relevant treatments.
Pathology reports govern more than half of the treatment procedures and the accuracy of these reports determine the effectiveness of therapies administered. Therefore, careful interpretation of pathological reports is crucial.
How does a pathological report look like?
A pathologist generates a report after blood/urine/tissue or any other body fluid sample testing and analysis. Every lab however has different terms and procedures for writing pathological reports.
However, in general, every lab will have the following mandatory sections:
- Patient information including – name, age, purpose, ID number or anything else that the lab may find important
- A brief medical history of patients with precise mention of related health issues
- Tissue description along with size, weight, appearance etc.
- Detailed description of tissue/sample during and after processing
- Final verdict and related diagnosis
Now, once you have undergone a laboratory test and have a report in hand, taking immediate doctor’s advice is essential. However, a slight knowledge of what the report infers can help you remain prepared for further procedures. And if at all you have no reasons to worry, you would definitely be happy to have decoded it yourself.
Below listed are 5 important pathological tests results explained:
Alpha-fetoprotein test:
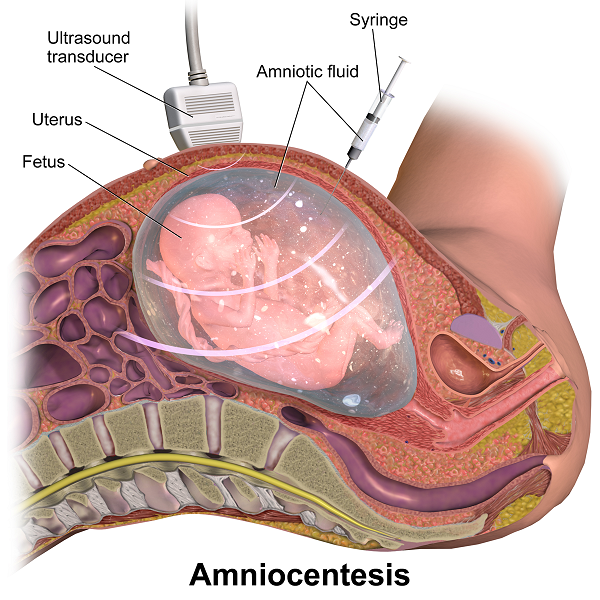
Alpha-fetoprotein amniotic fluid is a blood test conducted as a normal screening for pregnant women. The test is conducted in order to determine the amount of Alpha fetoprotein or AFP content in blood samples of pregnant women. However, the AFP test may also prove beneficial for adult men and non pregnant women.
AFP tests and results:
When conducted for pregnant women:
AFP test is usually conducted as a part of quad screening or triple screening test, that is carried out during the second trimester of pregnancy.
Alpha fetoprotein or AFP is produced by the liver of an unborn baby or fetus. This fluid produced, traces through the mother’s blood and therefore is detectable in a blood test conducted after 15 – 20 weeks of pregnancy.
Normal Range:
Pregnancy may lead to slight change in AFP levels; however, values ranging between 10 -150 ng/mL are considered absolutely normal.
Again, the AFP test results depend on the baby’s age. If the baby’s age is not properly determined, the results may appear to be erroneous. Mother’s height and weight, her general health condition etc. also influences test levels. Therefore, getting a doctor’s advice is crucial.
Levels above normal range:
AFP levels beyond permissible amount precisely indicate that the unborn baby may have certain birth defects. Chromosomal disorders such as; Down Syndrome, congenital problems, brain and spinal disorders; known as neural tube defects in the unborn baby, may all be determined by AFP and the quad test collectively.
A positive screening test result confirms that the baby has very high chances of developing any form of birth defect. Therefore, doctors do order for relevant diagnostic tests to confirm the result.
When conducted for non pregnant women or adult men:
As mentioned earlier, the test can also reveal essential health information for adults; both men and non pregnant women.
Normal range:
A healthy AFP level in this case lies between 0 – 40 ng/mL.
Levels above normal range:
High AFP levels can suggest a number of health related problems in adults. Some of them are:
- Cancer development in testicles, ovaries, pancreas or liver
- Brain tumors and lymphoma can also result in high AFP levels
- Patients suffering from acute Hepatitis B also show increased levels of AFP, if sudden Hepatoma or liver cancer symptoms are seen
Iron test/Serum test:
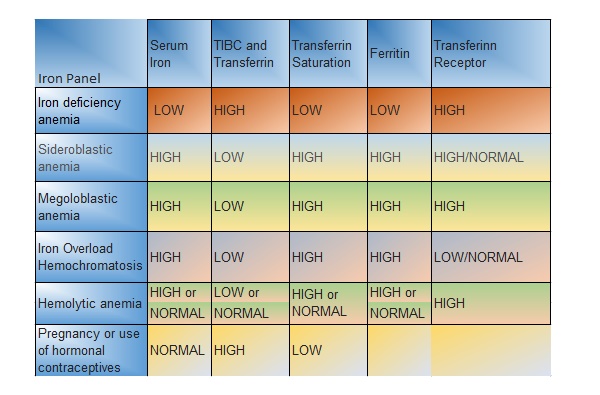
Iron test, also known as Serum Iron test, is conducted to determine conditions of iron deficiency or iron overload. This test is performed as a follow up test and is ordered only when other blood tests, such as – CBC or Hemoglobin tests have shown undesired or abnormal results.
Iron test is always performed in combination with other related tests; namely – TIBC(total iron binding capacity), transferrin and ferritin tests. Combined results obtained from these tests determine specific diseases related to iron levels within human body. For more information refer to the table below.
Normal Range:
Iron: Healthy reference level for serum iron are:
- Men: 65 to 176 µg/dL
- Women: 50 to 170 µg/dL
- Children: 50 to 120 µg/dL
- Newborns: 100 to 250 µg/dL
Total Iron Binding Capacity(TIBC): 250 to 370 µg/dL or 45 to 66 µmol/L
Transferrin Saturation:
- Males: 20 to 50 percent
- Females: 15 to 50 percent
Ferritin levels:
- Males: 20 to 250 µg/L
- Females: 15 to 150 µg/L
Abnormal test results:
Any variation from the above mentioned reference level may be a sign of underlying disorder that requires immediate medical attention. The table below explains abrupt levels and ailments they signify:
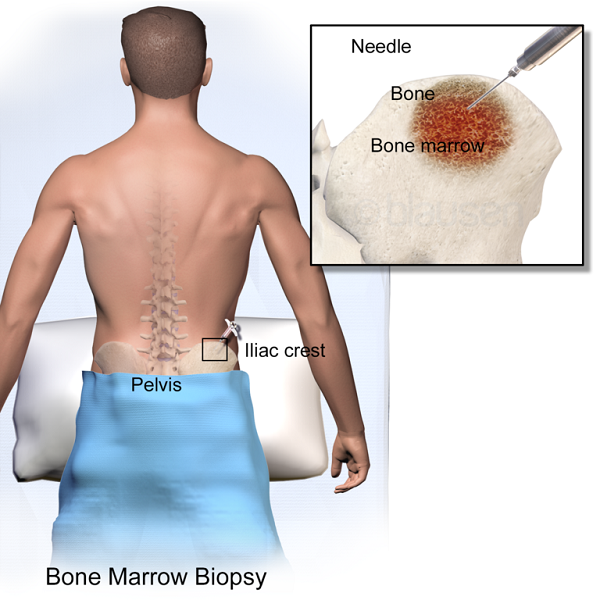
Bone marrow biopsy:
Bone marrow is a tissue present in the central part of bones that produce more than 200 billion red blood cells everyday; along with white blood cells and platelets. A bone marrow biopsy is a laboratory test performed to determine any disease or infection within the bone marrow.
Bone marrow samples are taken mostly from your hip bone; however, sometime chest bones are also used. The bone marrow has two parts – solid and liquid. When solid part of the marrow is taken, the process is known as biopsy while the procedure where liquid samples are tested, it is known as Aspiration.
Bone marrow biopsy test is one of the many tests that reveals serious and fatal health conditions, such as cancer. The doctor may order this test when blood test results show low RBC, WBC and Platelet count. A bone marrow transplant done accurately may save patients suffering from leukemia and lymphoma.
Understanding Bone marrow test report:
A bone marrow test report may have a multitude of health revelations to make. Some of them are:
- Our body has a definite proportion of RBCs, WBCs and platelets. Any variation in this proportion may lead to minor or severe disorders. A bone marrow test may help in identifying such dis proportionate levels leading to Anemia or Aplastic anemia.
Anemia is a condition where the bone marrow produces lesser number of RBCs in our body. It can also occur when body has scarcity of hemoglobin. It is a protein that carries oxygen from lungs to other parts of our body and also gives red color to blood.
Aplastic anemia is a condition where body fails at generating sufficient RBC, WBC and platelets.
Normal RBC Count:
- Men – 4.7 to 6.1 million cells/µL
- Women – 4.2 – 5.4 million cells/µL
Normal WBC Count:
4,500 – 10,000 per micro liter of blood
Platelets:
15,000 – 45,000 per micro liter of blood
- The blood cells that are generated gradually develop into mature/healthy cells. However, sometimes the body may have a marrow disorder where the cells refuse to mature. This leads to number of immature cells in body which are known as blasts. Myelodysplastic Syndrome is the medical term used for this condition, that can lead to Myeloid leukemia.
- The test also helps in determining metastatic cells and thus number of cancerous cell growth within body
D – Dimer test:
A blood test that detects the presence of unnecessary blood clot in body. Blood clotting is otherwise a healthy function that inhibits excess bleeding in cases of injury and cuts. However, when blood clots are formed frequently without reasons, they may lead to a number of serious health issues such as thrombosis.
D – dimer is a small protein fragment that appears in blood stream when blood clots are broken. The concentration levels in blood can be easily determined through D dimer test.
Normal range:
D – dimer concentration less than or equal to 250 ng/ml D dimer units (DDU) is considered to be healthy. Higher values may suggest health disorders; such as Deep Vein Thrombosis(DVT), Pulmonary Embolism(PE) and Strokes.
Urine Routine test:
Routine urine tests analyze urine compositions and identify alterations indicating number of health issues. Experts say that a simple routine urine test report can provide 100 different readings related to different functions and metabolic activities going within our body.
Urine test interpretation:
A sample of urine is tested on following factors that have been explained below:
Volume:
Normal range:
Early morning sample should range between 50 – 300 ml. This range is healthy; however, slight variations from this is also acceptable.
Abnormalities:
Levels beyond 500ml suggest cases of Diabetes and Polyuria. Again, levels below 20ml suggest kidney disorders
Color:
Normal:
Pale Yellow
Abnormalities:
- Dark yellow to orange, green or blue suggests liver disorder
- White suggests presence of pus
- Brownish black suggests rare disorders of melanin presence or homogenistic acid
pH values:
Normal:
4.5 – 7.5
Abnormalities:
Values less than 4.5 are more acidic and suggest cases of lung disorders and uncontrolled diabetes. Values more than 7.5 are more alkaline and suggest cases of kidney diseases, urinary tract infections etc.
Glucose:
Normal:
Absent or levels between 1 – 15 milligrams are acceptable
Abnormalities:
Anything above acceptable levels suggest cases of diabetes or Coronary thrombosis
Protein
Normal:
Absent
Abnormalities:
Traces are found in cases of heart diseases and kidney disorders
Crystals
Kidney stones are detected if crystals of calcium sulphate, calcium oxalate etc. are detected.
These were five important pathological tests with results explained. Understanding your blood test results or for that matter any other diagnostic test results is vital to remain vigilant about your health and welfare.
Thus, now that you have read this post, interpreting few things about your pathological test reports should be an easy task, isn’t it? However, do not skip visiting your doctor and pathologist to understand reports thoroughly.


Great explanation, each result is well described. Images have made it even more clear to understand. Knowing and understanding your pathological tests result is important, and your blog has explained really important one. Thanks for this informative post.