Frozen shoulder, medically termed as adhesive capsulitis, is a condition where there is inflammation in the lining of the shoulder capsule, thereby restricting movement of the joints. There is stiffness, pain and difficulty in moving the shoulder.
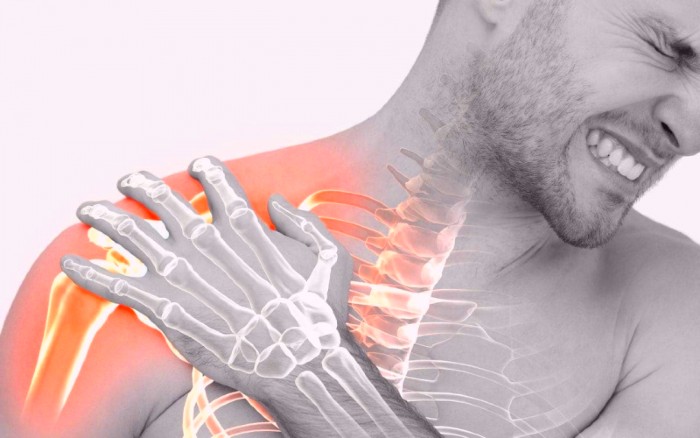
The shoulder is a ball and socket joint made up of three bones: humerus (the upper arm bone), scapula (shoulder blade) and clavicle (collarbone). The three bones are encapsuled in a strong connective tissue called the shoulder capsule. To smoothen the movements of the shoulder, synovial fluid lubricates the shoulder capsule and the joints. In frozen shoulder, this capsule becomes thick and inflamed, and results in stiffness and tightness. Adhesions, thick bands of tissues, develop, and less synovial fluid flows through. This causes the shoulder to become stiff and painful, and ultimately the movement reduces.
The signs and symptoms of frozen shoulder begin gradually and worsen over time and then resolve. This may usually take one to three years depending upon the severity of the issue. There is a significant loss of the shoulder’s range of motion in all the directions. Frozen shoulder causes long term pain and restriction of movements.
There is an increased risk of frozen shoulder if you have recently undergone a surgery, medical condition or a treatment that restricts the movement of the shoulders, for example a stroke or a mastectomy. Various conditions like Parkinson’s, hyperadrenalism, pulmonary disorder, stroke etc., contribute to frozen shoulder. Thyroid disorders like hypothyroidism increase the risk of developing frozen shoulder that is long lasting. Most commonly, frozen shoulder is seen among women in the age group 40-60 years. Women are more prone to developing a frozen shoulder than men.
Symptoms of Frozen Shoulder
The most characteristic symptoms of frozen shoulder are severe pain and the inability to move the shoulder even with someone’s help. There is achy, diffused pain. The pain is felt over the shoulder and along the arm. It begins gradually and increases with the movement. It is severe in the early stages and decreases in the later stages.
Later, the tightness of the shoulder capsule results in a noticeable change in the range of motion of the shoulder. Since, even a slight moment of arm can cause tremendous pain, people tend to avoid any movement. This results in immobility and causes more stiffness and pain. Moving the shoulder as much as possible reduces the stiffness and increases mobility. There is also trouble sleeping since the pain travels further down the arm making it extremely uncomfortable to fall asleep.
Phases of Frozen Shoulder
Frozen shoulder develops gradually and there are three phases you will go through. They are:
1. Freezing phase: In this stage, the pain gradually increases and keeps on increasing. The shoulder movements become restricted. The excess pain makes it difficult to sleep since the pain worsens at night. This usually lasts for about 6-9 weeks.

2. Frozen phase: In this stage, there is an improvement from the painful symptoms. However, the stiffness increases and this makes it hard to carry out daily activities. The inflammation, scar tissue and collagen buildup increases, causing extreme pain and stiffness. This lasts for about 4-6 months.
3. Thawing phase: The pain decreases gradually and motion range increases at a similar pace. However, the patient is relatively inactive, allowing for slow yet complete recovery. The thawing phase can last from 6 months to 2 years.
Causes of Frozen Shoulder
What causes frozen shoulder is not yet fully understood, although there are several medical conditions that can contribute to the development of frozen shoulder.
1. Diabetes: About 20% of the people suffering from diabetes; both insulin dependent and non-insulin dependent, are at a risk of developing frozen shoulder. Although the link is not quite clear, it is thought that the changes in the connective tissues because of high glucose levels is what increases the risk of frozen shoulder.
2. Other diseases: Other health issues like Parkinson’s, hypothyroidism, hyperthyroidism and cardiac diseases can also cause frozen shoulders.
3. Immobilization: Frozen shoulder can also result from immobilization of the shoulder for a long time; for example, if you’re recovering from a surgery, a fracture, or any other serious injury. Hence, doctors advise moving the shoulders as much as possible soon after the injuries, to avoid frozen shoulder.
People who have already suffered from frozen shoulder once are at an increased risk of developing frozen shoulder on the other side. Recurrence of frozen shoulder on the same side is rare and usually occurs on the other side. Although there’s a possibility of recurrence on the same side in people with health complications like diabetes.
Diagnosis of Frozen Shoulder
A physical examination is done to diagnose frozen shoulder. The examination is divided into two parts. The doctor will ask you to move your shoulder on your own. This is termed as active range of motion. The doctor might then advise you to relax while he/she moves your arm. This is termed as passive range of motion. Both the active and the passive range of motion are affected by frozen shoulder. In some cases, an anesthetic is injected by the doctor to check the passive and active range of motion.
Although frozen shoulder can be diagnosed by signs and symptoms alone, sometimes an X-ray or an MRI scan is suggested to rule out any other possibilities such as torn rotator cuff or osteoarthritis that can lead to pain and limited movements. But this is rarely done for frozen shoulder. It is mainly diagnosed on the basis of patient’s history and examination.
Treatment for Frozen Shoulder
There are several treatments for frozen shoulder.
The early treatment includes taking care of the shoulder and preventing it from being immobile. Physical therapy helps in regaining mobility in the shoulder. Physiotherapist can help in the recovery from frozen shoulder by teaching you a range of motion exercises to help you move the shoulder as much as possible. Strengthening and stretching exercises help deal with the stiffness and improve the range of motion. These exercises should be followed regularly to optimize recovery from the frozen shoulder.
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like aspirin, ibuprofen, can help in reducing inflammation and pain. In cases of severe pain, doctors may also suggest stronger pain killers and anti-inflammatory drugs to help you relieve the pain.

Corticosteroid injection is another treatment for frozen shoulder. This is usually recommended in the frozen phase, which is 3-6 months long. This injection is made up of two parts. One part is a corticosteroid, that temporarily reduces inflammation and improves the range of motion. Another part consists of an anesthetic called lidocaine that reduces pain.
Before the injection is administered, a local anesthesia is given to numb the area of administration. The radiologists use X-ray as a guide to make sure the injection is administered at the exact location in the shoulder joint. The procedure requires less than 30 minutes. Since corticosteroids have a tendency to increase blood glucose levels, it is important to administer the injection into the joint directly to avoid the risk of elevation.
Joint distention is yet another treatment. In this procedure, doctor injects sterile water into the shoulder capsule directly, which helps in stretching of the tissue and makes it easier to move.
Shoulder manipulation is a treatment procedure in which the doctor gives you an anesthetic and he/she will move the shoulder to ease the movements. Since you are under anesthesia and unconscious, you will feel no pain during the procedure.
Around 90-95% of the people suffering from frozen shoulder recover with non-surgical treatments like corticosteroid injections, NSAIDs, heat, and physical therapy. Undergoing surgery for frozen shoulder is rare and is only suggested when none of the non-surgical treatments work. In surgery, the scar tissue and adhesions are removed from the inner side of the shoulder joint.
Management of Frozen Shoulder
Most of the time, frozen shoulders recover on their own in a period of 6 months to a year. However, the pain and stiffness of the shoulder require regular exercise and movement. Stretching and strengthening exercises can help you manage a frozen shoulder more easily. It can help you maintain and regain mobility efficiently. Painkillers can also help in the management of inflammation and pain experienced. Trying to move the shoulder within the range of pain can also help in reducing the stiffness.
Contacting your physiotherapist or general practitioner can help you gain more support and insight in managing a frozen shoulder.





 Prescription medications include anti-depressants, sedatives, antihistamines, and melatonin receptor agonists. These medications have a variety of therapeutic effects and are often used to treat sleep disorders.
Prescription medications include anti-depressants, sedatives, antihistamines, and melatonin receptor agonists. These medications have a variety of therapeutic effects and are often used to treat sleep disorders.


 If you are taking a routine check-up that doesn’t usually need a prescription, you must note down this point. Before going for few tests, you may require to discontinue medicines that can alter your test reports. If you do not have any idea about the same, talk to the lab technician in advance.
If you are taking a routine check-up that doesn’t usually need a prescription, you must note down this point. Before going for few tests, you may require to discontinue medicines that can alter your test reports. If you do not have any idea about the same, talk to the lab technician in advance. If you are suffering from a serious disorder like HIV, you should let your lab technician know. This is because such diseases can spread through body fluids. Lab analysts must be extra careful with the blood samples of such individuals.
If you are suffering from a serious disorder like HIV, you should let your lab technician know. This is because such diseases can spread through body fluids. Lab analysts must be extra careful with the blood samples of such individuals.