Prostate Cancer Surgery
Listed below is the step by step procedure of prostate cancer surgery:
- What is Prostate Cancer Surgery?
- Why is Prostate Cancer Surgery required?
- Pre-operative Preparation
- Day Before Surgery
- Procedure Day
- Methods/ Techniques of Prostate Cancer Surgery
- Post Procedure
- Risks and Complications
What is Prostate Cancer Surgery?
Cancer of the prostate gland is known to be one of the most common forms in men. It can develop as a separate condition completely, or it can occur due to spread of cancer which has originally affected some other organ. It will lead to development of a tumor in the gland. The adjoining lymph nodes or surrounding organs may become cancerous too if the disease spreads. To avoid such issues, prostate cancer surgery is performed.
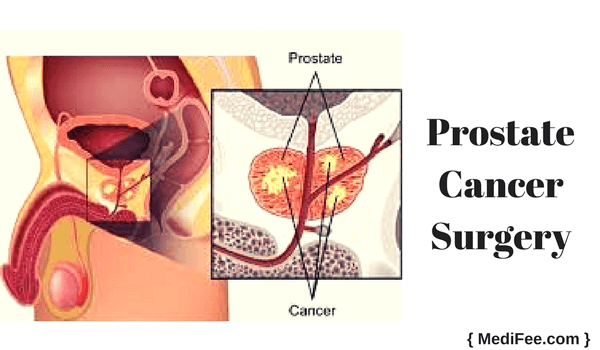
Surgery aims at treating prostate cancer by removal of the tumor along with the cancerous part of the prostate gland and the adjacent lymph nodes. Other surrounding organs to which cancer might have spread are also excised by surgery completely or partially. Surgery also aims at maintaining the functions of the remaining healthy prostate gland and other surrounding healthy organs as normal as possible.
Why is Prostate Cancer Surgery required?
Cancer of prostate gland is usually treated with medicinal mode, radiation therapy or surgery. The choice of treatment depends on patient's age, general health and stage of cancer. Staging is the process of determining intensity of the cancer depending on the presence and size of tumor, number of lymph nodes involved and spread to other organs.
Indications that surgery is needed:- Increase in symptoms:
Common symptoms of prostate cancer include difficulty in urination, increased frequency of passing urine, blood from urine. These symptoms might keep increasing despite treatment. In such cases, surgery may be indicated
- No response to other treatment:
Some cases of prostate cancer do not respond to medicinal therapy. There may also be some cases which are so advanced that they may not be suitable for medical treatment at all. These cases call for surgical intervention.
- Contraindication to other therapies:
At times, medicinal therapy or radiation therapy are not indicated in prostate cancer. The use of these modalities may be harmful to the patient's health. At such times, surgery is the most feasible option to be utilized.
- Recurrence of cancer:
Cancer of prostate may recur after it has been treated. Surgery can be employed to treat such recurrence.
Pre-operative Preparation
Surgery is always a well-planned procedure. It is not a rash decision which can be taken and implemented immediately. Every surgery needs consideration of multiple possibilities from point of view of the patient and doctor both.
Prerequisites for prostate cancer surgery
Once the decision for surgery has been taken, a lot of preparation is needed. Surgery is not the job of a surgeon alone. It takes a team of skilled nurses, anesthetist, surgeon and other assistant doctors to perform a surgery successfully. Cancer surgeries are often followed by pathological examination of the tissues which are removed. Hence, a pathologist is often part of the team which performs the surgery. Following prerequisites are to be fulfilled before the actual surgery is performed:
- Discussion
It is very important for the doctor and the patient to discuss the treatment options which are being utilized to treat prostate cancer. This ensures that the patient is relaxed as he/she knows what he/she will be undergoing. Also, such discussions are a way for patients to get all their doubts and fears cleared. Patients are also given an idea regarding the post-operative care, treatment and recovery period. They are made aware of complications or permanent disabilities which could possibly arise after the surgery. A signed consent form is needed to be obtained from the patient before finalizing the decision of the surgery.
- Admission to the hospital
Cancer surgery of prostate is not done on outpatient basis and needs the patient to be hospitalized. The reasons for this are various. The patient needs to be prepared for surgery. Certain investigative tests are mandatory to be performed prior to any surgery. These tests ensure that the patient is in good health and fit for undergoing surgery.
Tests like a complete blood count, blood sugar levels, liver function test, kidney function test, are performed to ensure proper functioning of the respective body systems. Blood grouping is also done. An ECG is advised to ensure smooth functioning of the heart. Chest X-Ray is also done most of the times. This ensures that the right type of blood is available if there arises a need for blood transfusion during the surgery following blood loss. A complete physical examination is mandatory before the surgery.
Day Before Surgery
Surgeries which involve use of general anesthesia, generally need the patient to have an empty stomach for a specific time prior to the surgery. This is because, when the patient is under anesthesia, there may be regurgitation (expulsion) if food is consumed. If this food enters the lungs, there could be serious respiratory complications.
Antacids are usually prescribed before the surgery to avoid development of acidity; again to avoid entry of stomach contents into the lungs. Laxatives may be administered to empty the bowels completely prior to surgery. Doctors generally advice the patients to avoid consuming food one night prior to the day of surgery. The patient's blood pressure, temperature, respiratory rate, pulse are monitored at regular intervals.
Procedure Day
The day of surgery is usually filled with anxiety for the patient who is nervous about its outcome. Well before the timing of surgery, the patient is taken to the operating room. Operating rooms are always sterilized to rid them of all infection before any surgery. All medical equipment, green gowns worn by the patient and doctor for the surgery, are sterilized as well.
The patient's blood pressure, pulse, body temperature and respiratory rate are measured before administering anesthesia and continued throughout till the procedure is finished. The type of anesthesia used for prostate cancer surgery is general. The type of anesthetic medicine to be used, the amount of medicine to be used, adjusting the dose of the medicine throughout the surgery, withdrawing the anesthetic medicine are all decided depending upon the patient's age, weight, stage of cancer, type of surgery and duration of surgery. Anesthesia is administered in the form of injections or in the form of fumes to be inhaled. The patient remains unconscious throughout the surgery.
The patient is draped in sterile surgical cloth. The skin of the area through which the surgery will be performed is exposed and marked. Prostate gland is often accessed by the skin over the lower part of the abdomen between the belly button to the pubis. Rarely the area of access is the skin between the anus to the scrotum. The skin through which the surgical incision will be made is prepped by shaving off all the hair over it. It is then splashed with ample amount of betadine solution which has antiseptic. This helps to get rid of small microorganisms which maybe present on the skin. After the anesthetist confirms that the patient is under the effect of anesthesia completely, the actual surgery begins.
Methods/ Techniques of Prostate Cancer Surgery
Following are the five types of surgeries which can be performed for prostate cancer:
- Open Prostatectomy
- Laproscopic Radical Prostatectomy
- Cryosurgery
- Bilateral Orchiectomy
- Transurethral Resection of Prostate (TURP)
Open Prostatectomy
Prostatectomy means removal of the prostate gland. Open surgery involves making a relatively big incision on the skin and accessing the prostate gland using various surgical instruments. In this type of surgery, the internal organs can be directly visualized. This surgery further can be done in 2 ways. The access point can be the skin between the belly button and the pubis. This type is done more commonly. The lesser often used route is via the skin between the anus and scrotum. Using this route may lead to problems in erection.
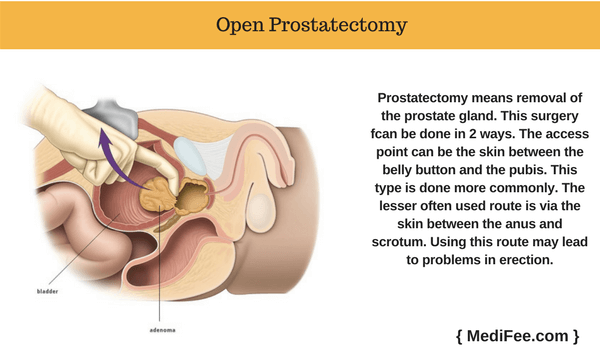
The skin is incised depending on the chosen route of access. The fat tissue, lying beneath is removed. Underneath is a layer of muscles which has to be cut very carefully to avoid permanent damage to the muscle itself and adjacent nerves and blood vessels. The tissue is carefully separated or cut till the prostate gland can be accessed.
Usually the seminal vesicles are removed along with the prostate gland. Adjacent lymph nodes are also removed to avoid spread of cancer to other regions. The tissue which was separated is kept in place again. Muscle incisions are repaired. The skin is closed with stitches, known in medical language as suturing.
Radical Laparoscopic Prostatectomy
This method differs from open surgery in that, the size of the incision made is much smaller. This ensures lesser blood loss and faster healing of the incision later. As opposed to open surgery which involves a single incision most of the times, multiple incisions are made in laparoscopic surgery. One incision is solely for the purpose of inserting a small video camera which helps the surgeon to visualize the internal organs so that they can approach the prostate gland in the correct manner. Other incisions are made to insert various surgical instruments. The further procedure remains the same as open surgery.

A variation in this method is robotic surgery. The surgeon does not essentially have to be present in the operating theater. Computer controlled robotic arms can be guided to move and perform the surgery through small incisions.
Cryosurgery
The word 'cryo' signifies cold. This surgery works on the principle of using very low temperatures to freeze and destroy the cancer cells; thus preventing their spread. This surgery can also be performed using regional anesthesia. This means that the patient is conscious during the surgery. Anesthetic medicines will be administered in a manner that only the nerve supplying a particular area of the body will become numb to any sensation. Through the skin between the anus and scrotum needles are inserted. Cold gases are released through the needles to destroy the cancerous part of prostate gland. Care is taken to avoid damage to the surrounding organs.
A catheter is usually inserted into the bladder and kept there for some days after the surgery to avoid urinary troubles. During the surgery, warm salt water is injected into the urethra to avoid it from freezing. It can be used effectively to treat early stage cancers. However its effectiveness has in advanced cases of prostate cancer has not been studied a lot. This surgery can also be performed on outpatient basis so that the patient does not need to be hospitalized every time. Blood loss is much less in this cryosurgery as compared to prostatectomy.
This surgery does not involve making big skin incisions. The prostate gland cannot be directly observed by the surgeon. This surgery can be performed under guidance of sonography.
Bilateral Orchiectomy
Bilateral orchiectomy refers to surgical removal of both the testes. This is done to obstruct the supply of testosterone to the prostate gland, thus preventing further development and spread of cancer. Testosterone is mostly manufactured in the testes. This process involves making a cut in front of each of the scrotum. Muscle tissue is cut properly to avoid damage. The testicular tissue is removed completely in simple surgery.
Another form of surgery known as subcapsular orchiectomy, involves removing only the testosterone forming tissue of the testicles. In both these methods, the penis and scrotum are left intact. This surgery is not advisable in young men who are in the reproductive age group. Sudden decrease in testosterone will inhibit their ability to reproduce. This surgery needs a lot of post-operative follow up as the reduced testosterone levels have a lot of side effects on the body. These have been listed in the article later. Medicinal aid may be needed to take care of the side effects. At times, the testes are replaced with artificial testes.
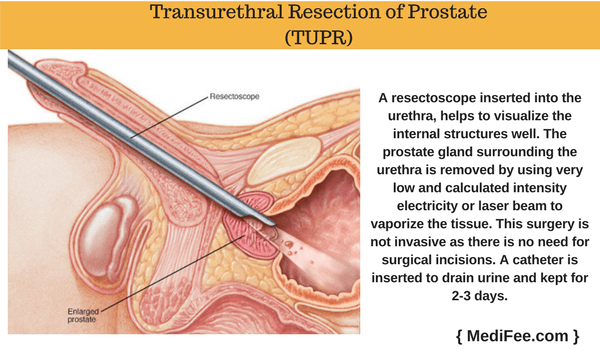
Transurethral Resection of Prostate (TUPR)
This procedure is not for treatment of cancer directly. It is used more often to treat non cancerous enlargement of prostate gland. In cases of cancer, it can be used to provide relief from symptoms of difficulty in passing urine. The access point is via the prostatic part of the urethra. A resectoscope inserted into the urethra, helps to visualize the internal structures well. The prostate gland surrounding the urethra is removed by using very low and calculated intensity electricity or laser beam to vaporize the tissue. Strict care is taken to prevent damage to the adjacent tissues. This surgery is not invasive as there is no need for surgical incisions. A catheter is inserted to drain urine and kept for 2-3 days.
Either of surgical methods are chosen by the surgeon depending on the age of the patient, the intensity of the cancer, other organs involved and general health of the patient.
Post Procedure
Completion of surgical procedures does not entail completion of treatment. Some short term and long term aspects to be taken care of are mentioned below. Faster recovery is possible if they are followed well.
Immediate Care
After the prostate surgery is over, the surgeon's job is done. But the anesthetist remains in the operating room. It is their job to taper off the anesthesia completely and check the patient's general health condition later. The blood pressure, heart rate, respiration, body temperature are monitored continuously till the anesthesia is withdrawn. Following postoperative care is usually expected:
- Immediately after the surgery, the patient is kept catheterized to aid easy passage of urine. The catheter is kept in place till the urethra heals. However, it should be monitored regularly to see if there is any bleeding and to check that it is in place. The catheter will usually be removed in some days.
- The patient is not given solid food immediately for the initial few hours if general anesthesia has been used for the surgery. The surgeon will examine the patient's bowel movements and then decide when to start solid food. The diet is usually kept simple for the first few days after surgery.
- It is advisable to include high fiber food in daily diet to avoid constipation. This can lead to straining of the intestines, which is inadvisable after surgery.
- Drinking plenty of water is advisable. This helps in preventing accumulation of urine in the bladder and thus preventing urine infections.
- Laxatives may be administered to patients to avoid discomfort while passing stool.
- Antibiotics and painkillers are administered as needed, most of the times.
- Follow up is to be done regularly as advised by the surgeon.
- The patient has to take care to avoid indulgence in sexual activity for a few days after surgery. It can be resumed later after consultation with the surgeon for the same.
Long Term Care
Depending on the type of surgery which has been used, the duration of recovery varies. Even after the patient has completely recovered, it is essential that he remains aware and cautious about his/her health. The doctor usually gives a detailed explanation of the things that the patient should be aware of.
Cancer patients are usually called for regular follow ups for a long period to judge whether the cancer has recurred in the same organ again, or if it has started developing elsewhere.
At times, cancer has not resolved or reappears. In such cases, any of the forms of therapies which have been explained above may be used by the doctor depending on each individual case.
Monitoring maybe done by undergoing MRI scan, CT scan, sonography and PSA test at intervals designated by the doctor.
Risks and Complications
Every treatment method comes with its set of disadvantages and complications. All complications are not essentially seen in each case. There may be cases with no complications at all. In some cases, a combination of the following complications may be seen in varying intensity:
Loss of fertility, hot flashes (sudden experience of heat, palpitations and sweating), anxiety and depression, gynecomastia. (development of breasts in men), weight gain, problems with erection of penis may occur following bilateral orchiectomy. These need to be treated with hormonal therapy.
Inability to reproduce may be a consequence. This could be due to reduced testosterone supply, reduced sexual desire, reduced erection of penis or a combination of all of the above. Proper treatment, using medications, is given to revert these problems.
Difficulty in passing urine can occur in case of all above mentioned surgeries since the urethra is involved. This problem usually resolves on its own. If not, the patient should follow up with the surgeon.
Sudden urges to pass urine occurring too frequently, inability to control urine flow may be experienced.
There could be accidental injury to healthy part of prostate gland or adjacent healthy organs.
Damage to blood vessels could lead to excessive blood loss. Hence, blood is always kept ready for transfusion in almost all surgeries.
There could be allergic reaction to the anesthetic medicines used. Appropriate medicinal treatment may be essential for it.
Passing blood from urine is commonly noticed after TURP surgery. If it does not resolve automatically, the surgeon should be consulted.
More information related to Prostate Cancer surgery
Best Uro Surgeons in India
Top Cancer hospitals in India

