Bone Marrow Transplant
Listed below is the step by step procedure of bone marrow transplant:
- What is Bone Marrow Transplant?
- Why is Bone Marrow Transplant Required?
- Pre-operative Preparations
- Day Before Surgery
- Procedure Day
- Methods/Techniques of Bone Marrow Transplant
- Post Procedure
- Risks and Complications
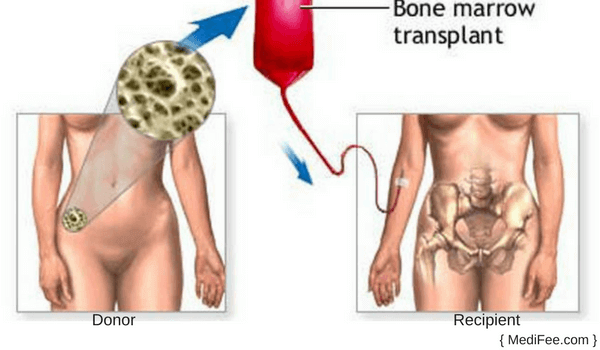
What is Bone Marrow Transplant?
Bone marrow may get damaged because of infection, disease or chemotherapy. To replace this bone marrow, new stem cells are transplanted. These new stem cells produce blood cells and help in promoting growth of new marrow. This process comprises bone marrow transplant.
Why is Bone Marrow Transplant Required?
Primary reason for bone marrow transplant is unhealthy bone marrow. Chronic infection can cause bone marrow to become weak over a period of time. Chemotherapy which is generally used as a treatment method for cancer can also destroy healthy bone marrow cells. Listed below are factors which might prompt need of bone marrow transplant.
Aplastic anemia
Disorder wherein bone marrow ceases creating new blood cells.
Leukemia
It is the cancer of blood forming tissues or bone marrow. Person suffering from leukemia has abnormal production of blood cells, generally that of white blood cells.
Lymphoma
It is the cancer of lymphatic system. It is specifically cancer of lymphocytes which are a type of white blood cells. Since, these white blood cells are manufactured in bone marrow, bone marrow transplant can be implemented as a treatment method for lymphoma.
Multiple myeloma
It is cancer of plasma cells which are an important part of immune system. These cells can be found in bone marrow and hence, bone marrow transplant could be a potential treatment for multiple myeloma.
Chemotherapy
This cancer treatment targets cancerous cells. High doses of chemo drugs can affect bone marrow and destroy its ability to produce new blood cells.
Congenital neutropenia
Congenital means the disease is present since birth. Congenital neutropenia is a disorder wherein infection keeps on recurring.
Sickle cell anemia
Type of anemia that occurs because of abnormal shape of red blood cells. These red blood cells transport less oxygen and patient becomes tired easily. As a way of sickle cell anemia treatment, bone marrow transplant option is considered.
Thalassemia
Inherited blood disorder wherein body manufactures abnormal type of hemoglobin. Hemoglobin is an important constituent of blood and is responsible for oxygen supply to each and every cell in the body.
Recurrent exposure to radiation
Radiation therapy is often a choice of treatment for patients who are cancer patients. Though it is beneficial for the patient, radiation therapy comes with some side effects, Chronic exposure to radiation may lead to damage to the bone marrow. This is one of the indications for bone marrow transplant. People working in fields which require them to be exposed to radiation for a long time are also victims of this problem.
Pre-operative Preparation
Doctor will hand over a list of tests to be conducted before bone marrow transplant in order to determine what type of bone marrow cells are required to be transplanted. If you are a cancer patient, doctor may suggest you few rounds of chemotherapy or radiation therapy to kill all cancerous cells before bone marrow transplant procedure commences. This is known as conditioning regimen.
Here is a list of few tests that are conducted prior to bone marrow transplant procedure to avoid any potential chance of infection.
- CBC (Complete Blood Count)
- Pulmonary function tests
- Tests such as electrocardiogram and echocardiogram that help in evaluating heart condition
- Chest X-ray
- CT Scan (Computed Tomography Scan)
- Bone marrow biopsy
- Evaluating health condition of skeletal structure
- Complete dental checkup
Since, bone marrow transplant procedure is quite complex, you will be required to stay in the hospital for a long period of time. You need to take care of your financial concerns and arrange for insurance coverage.
Day Before Surgery
Day before the surgery, doctor gives you a brief idea about the surgical procedure and how it's going to shape up. Arrangement for blood transfusion should be made on the day before the surgery since the possibilities of excess blood loss cannot be ignored.
You make ask for support of your loved ones to overcome this difficult phase. Emotional support will help you to pull through and keep anxiety at bay.
Diet before the day of surgery should be discussed with your doctor and followed accordingly.
Procedure Day
On the day of surgery, vital signs such as blood pressure are monitored. It's important that your blood pressure is at optimal level or within normal range to avoid any complications during the surgery.
Methods/Techniques of Bone Marrow Transplant
There are two methods through which bone marrow transplant can be carried out - Autologous Transplants and Allogeneic Transplants. Let us understand these techniques in detail.
Autologous Transplants
As the name suggests, this procedure makes use of patients own stem cells to form new blood cells. Stem cell harvesting has to be done before autologous transplant procedure is implemented.
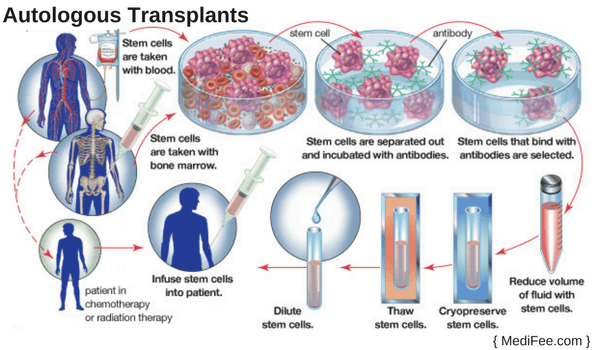
Stem Cell Harvesting
For stem cell harvesting, peripheral blood stem cells that circulate in the blood are collected and harvested. Through mobilization treatment, stem cells from bone marrow can be passed into bloodstream. Then the collection process commences once stem cells enter into the bloodstream.
The process of separating blood takes few hours and is conducted using apheresis machine. Once, the required amount of stem cells are collected, they are harvested and frozen in Stem Cell Processing and Cryopreservation Laboratory. They are kept in the laboratory until they are ready to be harvested.
Just like the process of blood transfusion takes place, frozen bags of stem cells are thawed and then transplanted. The stem cells travel to bone marrow and then eventually start producing new blood cells. This process is called engraftment.
Eventually, blood production will increase. Need of blood transfusion may arise owing to less blood count in initial phase. Patient health condition will be monitored once the procedure gets completed to check for infection or complications. Blood tests will be conducted for weeks post procedure to check if blood count has increased or not.
Allogenic Bone Marrow Transplant
Generally, allogeneic bone marrow transplant procedure is implemented to treat blood cancers and other complicated, serious disorders, such as leukaemia and its types, myeloma, myelodysplastic syndromes, lymphoma, aplastic anaemia and other rare type of bone marrow diseases.
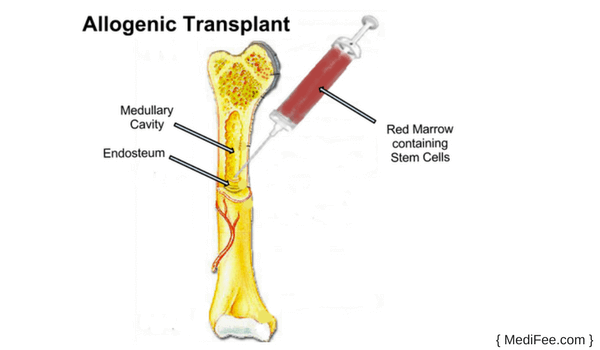
In allogenic bone marrow transplant, patients own stem cells are not used but are donated by genetically matched stem cell donor. Thus, the donors mostly are your family members - brother or sister. If no family member is available, unrelated stem cell that is suitable to the patient's body is transplanted.
Allogenic bone marrow transplant replaces receiver's affected or damaged stem cells with healthy stem cells donated by the donor. Stem cells get damaged because of exposure to high doses of chemotherapy and radiation therapy. White blood cells present in donors blood are also transplanted along with stem cells so that compatibility is increased and underlying disease is also cured.
Complexity of this procedure increases when donor is not genetically related. Even slightest difference of unrelated stem cells can cause complications. Hence, for patients above the age of 60 or those who are suffering from serious illness, allogeneic bone marrow transplants are not recommended.
In case of senior citizens for whom allogenic bone marrow transplant can prove to be too risky or those who can benefit from receiving stem cells, 'mini-allogeneic' or 'reduced intensity' transplants can be used as an alternative option. The procedure is of less intensity since it does not completely destroy bone marrow. It is especially beneficial for patients suffering from bone marrow cancer since the donor's immune system (consisting of white blood cells) will help in killing receivers cancerous cells. Also, underlying diseases will be suppressed reducing chances of rejection by the host's body.
Since, the procedure involves donor to donate stem cells, he/she is given a series of injections called Granulocyte Colony Stimulating Factor (G-CSF). The injections are generally given over four days distributed in four doses to stimulate stem cells to enter into blood stream. Once the stem cells or Peripheral Blood Stem Cells (PBSC) gather in required proportion in bloodstream, they will be extracted by using apheresis machine which is attached to the donor. The procedure is painless and donor can resume normal activities on the same day itself.
During transplant, donated stem cells are infused into the patient's bloodstream through vein. The procedure is similar to blood transfusion. Once, the stem cells enter into the receiver's bloodstream, they travel to bone marrow and get settled down and eventually start producing new blood cells.
A week after the procedure, blood count may drop drastically. Hence, chances of infection are high during this period. Medications and sometimes, blood transfusions may be recommended to the patient to help cope up with low blood count.
Post Procedure
It takes approximately an year to completely recover post surgery. The first 100 days post treatment are crucial wherein maximum complications can occur. Note that recovery process for every patient will be different. Some may venture smoothly while some may face hurdles.
Recovery will happen slowly and you must adhere to below mentioned tips in order to ensure smooth recovery:
Check for infection
Post bone marrow transplant, chances of infection increase; especially if the body has not responded well to the procedure. If infection occurs, patient has to consult with doctor so that other curative options can be employed to curb it. Hence, taking care that infection does not occur helps in reducing complications. Immunity in first three months may be low but, with time and with proper care, immunity power can be increased. Infections can be serious and sometimes, can become fatal.
Graft Versus Host Disease (GVHD) is a common complication that occurs after allogeneic transplant. If it occurs within 100 days of the transplant, it is called as acute GVHD, and if it occurs after 100 days, it is called chronic GVHD. In this complication, immune cells from donated bone marrow are not able to identify hosts cells and hence, as a defensive measure, attack them.
Paying close attention to hygiene is of paramount importance. Daily bathing is the first defense mechanism you can use against bacteria that sits on your skin. Oral hygiene must also not be ignored. Brushing twice a day - once in the morning and before going to bed at night is important to get rid of food particles that might have settled between the spaces present in teeth. These food particles rot in these spaces and are responsible for bad breath. Flossing after meals should be a habit.
Avoid coming in direct contact with dirt and grime. Wash your hands thoroughly before you have your meals and after you visit toilet. If you are outside, you can cleanse your hands with use of sanitizer.
Follow up procedure
Follow up procedure should be strictly adhered to. Patients who have undergone extensive and complex bone marrow transplant surgical procedure, may be required to visit hospital on everyday basis for some therapies. Other patients have to follow guidelines suggested by the doctor and take medications on time. Periodical appointments with doctor have to be structured to check for development or any complication. If you notice any of the following symptoms consistently for few days, make it point to show it to your doctor.
- High fever of 37.8°C (100°F) for patients who have undergone allogeneic bone transplant surgery and 38.0°C (100.5°F) for autologous bone marrow transplant patients
- Dry cough or consistent cough with green or yellow sputum
- Shortness of breath
- Redness or swelling in the region where central venous catheter is placed
- Diarrhea
Diet
It is said that you are what you eat. Recovery after bone marrow transplant becomes smooth if you consume healthy diet. Include foods rich in iron such as green leafy vegetables, dates, beef liver etc. in your daily diet to increase count of red blood cells. Make sure that you consume some source of vitamin C after you eat iron rich food to enhance absorption of iron into the body. Iron that is obtained from plant sources is quite difficult to be absorbed as compared to iron that is obtained from animal sources. Hence, doctor may recommend the patient to consume meat in order o prevent anemia which is iron deficiency disease.
Exercise
Exercise is crucial for body to recover. In the initial phase, you may not be able to do much vigorous exercises. Exercises, such as walking, swimming, yoga etc. which do not put undue strain on muscles should be done on daily basis. You can start your exercise regime by walking slowly and gradually increase intensity and time duration.
Risks and Complications
Bone marrow transplant procedure involves certain risks and complications. However, they can be eliminated with proper medications and treatment. Common risk and complications that occur post bone marrow transplant are:
- Infection
- Stem cell (graft) transplant may fail
- New type of cancer may evolve
- For allogeneic transplant patients, there are chances of Graft Versus Host Disease (GVHD) developing
- Organ damage
- Infertility
- Cataract
- Bone marrow transplant in very rare cases might prove fatal. This happens if the body does not even slightly react positively to transplanted stem cells.

