Spinal Decompression Surgery
Listed below is the step by step procedure of spinal decompression surgery:
- What is Spinal Decompression Surgery?
- Why is Spinal Decompression Surgery Required?
- Pre-operative Preparation
- Day Before Surgery
- Procedure Day
- Methods/ Techniques of Spinal Decompression Surgery
- Post Procedure
- Risks and Complications
What is Spinal Decompression Surgery?
Surgery to restore normal inter-vertebral gap is known as spinal decompression surgery. Spinal cord passes through the vertebral column which comprises of many vertebral bones. Between two adjacent vertebral bones, is a layer of cartilage. It offers cushioning and avoids friction between the bony surfaces directly. Sometimes the cartilage gets eroded, compressed or prolapsed and the normal gap between two vertebrae is reduced. This may cause discomfort to the patient.
Spinal decompression surgery procedure involves surgical manipulation of the vertebral bones. Sometimes the cartilage can be operated upon. A number of reasons could result in reduced gap between the vertebrae, thus necessitating the surgery.
Why is Spinal Decompression Surgery Required?
Through the center of the vertebral column, passes the spinal cord. Nerves branching out of the spinal cord, come out through the gap between two adjacent vertebrae. Reduction in the gap will compress the nerves and cause symptoms. This is the main pathology which has to be treated by spinal decompression surgery. Some indications of surgery for releasing spinal compression are given below:
- Prolapsed Inter-vertebral Disc:
Commonly referred to as 'Slipped Disc,' this condition causes the cartilage between two adjacent vertebrae to be displaced from its normal position. This could happen due to excessive strain on the particular region of spine. The lumbar vertebrae are most commonly affected by this condition. They correspond the back and lower back of human body. Lifting of heavy weights, bending forward too often for a long duration are most common reasons for this.
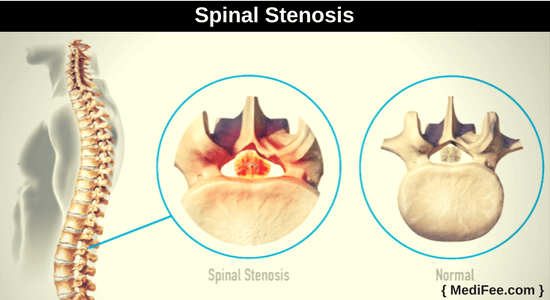
- Spinal Stenosis:
Spinal stenosis means narrowing of the lumen (diameter) of the spinal canal which contains the spinal cord. This will cause the spinal cord to be compressed. In turn, the nerves leaving the spinal cord will also be compressed which will lead to corresponding symptoms.
- Erosion of Cartilage:
Wear and tear of the cartilage which forms a cushion between two adjacent vertebrae may occur due to over strain on the vertebrae. This is seen more in the vertebrae of lower back. Reduced height of the cartilage will lead to reduction in the gap between the vertebrae. Nerves coming out of this gap can get compressed.
- Calcification of Joints:
Adjacent vertebrae form a joint with each other. Sometimes, due to certain disease, there may be deposition of excess calcium around the joints, which may cause their thickening. The thickened joints can be a cause of compression of spinal cord or the nerves arising out of the cord.Adjacent vertebrae form a joint with each other. Sometimes, due to certain disease, there may be deposition of excess calcium around the joints, which may cause their thickening. The thickened joints can be a cause of compression of spinal cord or the nerves arising out of the cord.
- Unresolved Symptoms:
Compression of spinal cord or its nerve roots will lead to pain, numbness, tingling, weakness. These symptoms are usually felt in the region which is controlled by the nerve which is compressed, Sometimes the symptoms resolve after taking medicines or physiotherapy sessions. At times when these methods fail to provide relief, surgery might be needed.
Pre-operative Preparation
Spinal surgery is a major and complex procedure. It needs to be done with great caution. A lot of details have to be considered while performing the surgery. Operating upon the spine is very tricky since there are many nerves in the surrounding area. If any nerve was to be mistakenly damaged, there could be some impairment of some important functions associated with that nerve. While planning for the surgery, importance is given to the following points:
- Discussing the Surgery
The surgeon has to discuss the surgery with patients and their immediate family before finalizing the decision. The patient needs to be explained the surgery in detail. A signed consent form is generally taken from the patient before surgery.
- Type of Anesthesia
Spinal decompression surgeries can be performed under general or spinal anesthesia. The choice of anesthesia depends on the patient's condition, health, age, extent of spinal compression. Final decision is taken by the anesthetist and surgeon together.
- Investigations
Spinal surgery is likely to be associated with severe blood loss. Hence, prior to surgery, test is done to determine the patient's blood group. Blood matching the patient's group is kept ready in case transfusion is needed. White blood cell count is determined. If it is high, it is indicative of some infection. Surgery is withheld till the infection is controlled. High blood sugar levels also contraindicate surgery. X-Ray or CT scan of the spine gives an idea about the location and extent of spinal compression. Kidney function and renal function tests rule out any abnormalities in the functioning of kidney and liver respectively. Blood tests are also done to determine the clotting time. This gives an idea about how long it will take for the patient's blood to naturally clot after being exposed to external environment.
- Medicines
Patients who are to undergo spinal surgery may be taking medicines for other conditions. These medications should be discussed with the surgeon. Some medicines may interfere with the action of anesthetic agents used for the surgery. Their dose might be altered before and for sometime after surgery.
Day Before Surgery
It is advisable for patients to be admitted to hospital a day before spinal decompression surgery. From the night before surgery, patients are asked to not eat anything. This is to avoid complications during surgery. General anesthesia renders intestines paralyzed for the duration of surgery. If any intestinal contents are present, during surgery they may come out of the esophagus and enter the lungs via wind pipe. This could cause breathing complications. Sometimes laxatives are given prior to surgery to clear out the bowels. Antacids are prescribed to prevent reflux of acid from esophagus into the oral cavity or trachea. A complete physical examination is done prior to surgery. Patient's blood pressure, body temperature, pulse rate, breathing are monitored after set time intervals.
Procedure Day
On the day of surgery, the patient is taken to the operation theater. Proper sterile attire provided by the hospital has to be used for surgery. For spinal surgery, patient is positioned face down on the operating bed. Arms are to be placed at the side in a way that no nerve gets compressed for the duration of surgery. If regional anesthesia is administered, the surgeon injects it into the spine through the lower back. If general anesthesia is administered, this is also given in the form of an injection. It is administered through a vein in the arm. In case regional anesthesia is used, the patient will remain conscious throughout the surgery. However, there will be no sensation at the area which is being operated upon. In case of general anesthesia, the patient will be completely unconscious.
Methods/Techniques of Spinal Decompression Surgery
Spinal decompression surgery is mostly performed upon the lumbar vertebrae. These correspond to the back and lower back in human body. Sometimes, vertebrae in the neck may need decompression surgery as well. Following are the types of surgeries for decompression of spine:
- Discectomy
This is the choice of surgery for 'slipped disc.' When the disc of cartilage between two vertebrae protrudes from its normal position, surgical methods are employed to remove the displaced disc. The surgeon will cut the skin over the affected vertebrae. The portion of the cartilage which is compressing either the spine or the corresponding nerves, is removed surgically. This releases the pressure over the spine or nerves.
- Laminotomy
Lamina is a part of the vertebral bone which is in direct touch with the spinal canal. Sometimes, making a hole surgically, on the lamina, helps to relieve some pressure on the compressed spine or nerves. This is the principle of laminotomy. The surgeon makes an incision on the skin near the vertebra which is to be operated on. The lamina is exposed and a hole is drilled carefully in order to give extra space to the compressed spine or nerves.
- Laminectomy
In this procedure, a part of the lamina or the whole of it is removed surgically. The procedure is the same as that of laminotomy. The difference is in the end result. Instead of creating a hole in the vertebra, it is surgically removed.
- Foraminotomy
The word foramen means opening. Between two vertebrae, there is a foramen for the exit of nerves which arise from the spinal cord. This opening might become smaller due to thickening of the vertebrae, protrusion or displacement of cartilage or some other cause. Foraminotomy is done to expand the opening, thus allowing the nerves more space to exit the spinal canal. Foraminectomy is also another procedure where a large portion of bone or cartilage is removed. The procedure to access the vertebrae is the same as mentioned in the previous surgeries.
Depending on the location and degree of damage involved, the most appropriate method can be chosen for each individual case. All the above procedures can be done by open method. They can also be done using an endoscope. Endoscopic procedure can be performed by giving multiple small incisions on the skin. They are minimally invasive surgeries and do not require extra exposure of the internal organs. Following surgery, the patient takes some days to weeks for recovery. During this period, certain health restrictions are advisable to be followed. Extra care has to be taken till complete recovery is achieved.
Post Procedure
After Surgery is CompletedAfter completion of surgery, patient is shifted from the operation theater. If spinal anesthesia is given, there may be numbness felt in the lower part of body for sometime after surgery. If general anesthesia is used, the patient will remain unconscious for sometime after surgery. When the effects of anesthesia wear off, a general physical examination is performed. The surgical wound is checked for bleeding or any other abnormality.
Caring for the Surgical IncisionThe surgical incision is closed after surgery using a special type of thread. The incision has to be kept clean, dry and closed with dressing. It has to be checked for signs of bleeding or infection. If any of these are observed, patient must consult with a doctor immediately.
Rest and Physical ActivityIt takes some days to weeks for complete recovery after spinal decompression surgery. During this period, it is advised to take as much rest as possible. The patient should not indulge in lifting heavy weights, doing strenuous exercises, or straining the spinal muscles in any manner. At the same time, care has to be taken that the patient does not remain totally sedentary (seated or inactive). This might render the spinal muscles stiff. Walking around, doing work which will put no pressure on back muscles may be done with the surgeon's advise.
PhysiotherapyAuxiliary mode of treatment like physiotherapy can be started to exercise the back muscles in a way that they get toned but are not strained. Physiotherapists advise treatment in the form of exercises, heat therapy, traction therapy and a few other methods.
MedicationsThere is possibility of infections after spinal decompression surgery at the site of surgical incision. Pain is often felt at the site of incision too. Pain killers and antibiotics are prescribed for the same.
These precautions aid in successful and fast recovery after spinal decompression surgery. They also help to avoid complications which could arise after surgery. However, sometimes, even despite of all precautions, patients could face some health issues due to complications which occur during or after surgery.
Risks and Complications
Spinal decompression surgery is associated with some risk factors. These could occur during or after the procedure. However, they can be treated. Some of the complications are mentioned below:
- Bleeding and Blood Clots
During surgery, the equipment which is used could injure some blood vessel passing adjacent to the vertebrae to be operated upon. This could cause bleeding. Blood can obscure the view during surgery and needs to be drained. In case blood loss is excessive, balance can be restored by performing blood transfusion. The accumulated blood soon clots. To dissolve the clots, blood thinner medicines can be taken.
- Infections
Spinal decompression surgery can lead to infection at the site of surgical incision or even in the internal organs which are operated upon. Antibiotics are prescribed to treat infections.
- Allergy Due to Anesthesia
Anesthetic agents could cause allergic reaction in some patients. This may be in the form of skin rash, breathing troubles, itching. If this happens, the anesthesia is stopped. Another agent is used. Anti-allergic medicines which suit the patient's constitution are administered at the earliest. Blood pressure has to be monitored continuously during surgery in such patients.
- Injury to Nerve
Spinal decompression surgery is done to release on the nerves or the spinal cord. During the surgery, the affected nerve could get injured. This can cause symptoms like weakness, pain, numbness, tingling along the course of that nerve. Medicines and physiotherapy can help to curb these symptoms.
More information related to Spine Surgery
- Information on Spine Surgery
- Information on Spinal Fusion Surgery
- Information on Laser Spine Surgery
- Information on Cervical Spine Surgery
- Information on Laminectomy
- Information on Lumbar Discectomy
- Information on Lumbar Puncture
- Information on Vertebroplasty
Cost of Spine Surgery in India and top cities
List of best Spine Surgeons in India and top cities
List of best Orthopedic Hospitals in India and top cities

