Mitral Valve Replacement Surgery
Listed below is the step by step procedure of mitral valve surgery:
- What is Mitral Valve Replacement Surgery?
- Why is Mitral Valve Replacement Surgery Required?
- Pre-operative Preparations
- Day Before Surgery
- Procedure Day
- Methods/ Techniques of Mitral Valve Replacement Surgery
- Post Procedure
- Risks and Complications
What is Mitral Valve Replacement Surgery?
Mitral valve dysfunction sometimes needs to be treated with surgical intervention. The method of surgery is known as mitral valve replacement surgery.
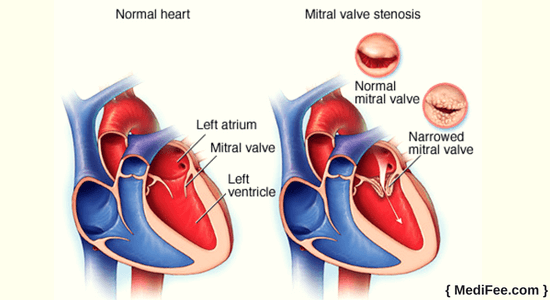
Human heart is divided into 4 chambers. The upper chambers are known as the atria and lower chambers are known as ventricles. Mitral valve also known as bicuspid valve lies between the left atrium and left ventricle. In a normally functioning heart, the left atrium receives oxygenated blood from lungs. The blood then enters the left ventricle when mitral valve opens. From the left ventricle blood is pumped out by the heart to all other organs. A healthy mitral valve will open only in one direction and allows passage of blood only from left atrium to the left ventricle.
If there is any defect in the valve and it fails to function normally, it is replaced surgically with a new artificially synthesized valve or a biological valve. There are several health conditions which necessitate mitral valve replacement surgery.
Why is Mitral Valve Replacement Surgery Required?
Mitral valve replacement surgery can be considered in a patient if any of the following conditions are present:
- Mitral Stenosis:
Stenosis is a condition in which the mitral valve opening becomes narrow. The valve consists of two leaflets. This could happen because the leaflets of the valve fuse together and become rigid.
- Mitral Regurgitation:
Mitral valve might lose its normal structure and firmness. It may allow back-flow of blood from the left ventricle to left atrium. This condition is known as mitral regurgitation.
- Unresolved Symptoms
Due to mitral valve defects, there could be symptoms like elevated blood pressure, breathlessness, rapid heartbeat, swelling of ankles, wrists or the entire body feeling faint. Mitral valve defects are at times asymptomatic. If however symptoms are present and they do not resolve with other treatment methods, mitral valve replacement surgery might be used.
- Failure of Mitral Valve Repair Surgery
Mitral valve defects can be surgically repaired. Valves can be tightened in case of mitral regurgitation to make them firm. In case of mitral stenosis, the fused valves are separated. If the valves have swollen in size or have calcium deposits, they are resized by removing extra tissue and deposits. Valves are attached to the wall of the heart by cords. Sometimes, strengthening the cords suffices in restoring the function of mitral valve. However, there is possibility of these procedures failing at times. As a end resort, surgical replacement of the valves has to be done.
Mitral valve replacement surgery can be performed if the patient fulfils any of the above mentioned criteria. There are certain procedures to be completed before the surgery can be started. They ensure that the surgery is performed with least possible complications.
Pre-operative Preparation
Surgery cannot be performed as soon as it is decided. It needs planning which begins days before the actual procedure. Some of the pre-surgical preparations have been described below:
- Discussing With the Patient
Though it is the surgeon's final call to perform surgery, it is important to discuss about it with patients. The patient must sign a written consent form to say that they are willing to go ahead with the surgery.
- Investigations
There are certain investigations which need to be done before mitral valve replacement surgery. These include blood group determination, white blood cell count, blood sugar levels, kidney and liver function tests. Blood matching the patient's group is kept ready prior to surgery. It may be used for transfusion in case of severe blood loss. All the tests must be within normal limits before surgery. A chest X-Ray gives a fair idea about the size and shape of heart.
- Medicines
Prior to surgery, the surgeon and patient discuss about all the medicines the patient might be taking for any other health conditions.
Day Before Surgery
The day before surgery is very important. Any last minute preparations which might have been missed out, are completed on this day. The patient is advised to get admitted to the hospital a day before the surgery. Laxatives and antacids are started a day prior to surgery. This is done to empty the digestive tract of its contents. During mitral valve replacement surgery, the patient is under the effect of general anesthesia. Digestive system becomes temporarily paralysed. A full intestine can cause trouble in such a case.
A complete physical examination is done before surgery. Blood pressure, pulse rate, breathing rate, are monitored at regular intervals.
Procedure Day
On the day of surgery, the patient is wheeled into the operating room prior to the decided time of surgery. Sterile surgical gown is given to the patient to wear. The patient's blood pressure, heart rate, breathing and body temperature are monitored. Anesthesia will be administered to the patient in the form of injection or nasal fumes. The patient is completely unconscious after a few minutes. Surgery can be started only after the anesthesia has completely set in. Before the surgery, the skin where the surgical incision is to be given is shaved properly to rid all hair over it. It is then cleaned with an anti-septic solution to kill all microorganisms in the skin.
Methods/ Techniques of Mitral Valve Replacement Surgery
Surgery can be performed by using either a mechanical valve or a biological valve. A mechanical valve is made of artificial material. A person receiving a mechanical valve transplant has to take blood thinning medications for a long time after surgery. This is because the material of the valve could lead to formation of blood clots. Biological valves are synthesized from natural body tissue of animal or human origin. They have lesser durability, but the patient does not require to take blood thinners as the possibility of developing blood clots is very less.
- Open Surgery
A single long vertical cut is made at the center of the chest. The breast bone is removed and the underlying muscles are carefully separated. A heart-lung machine is used. It performs functions of the heart for the duration of surgery. Heart is kept in a state of immobility as it is difficult to operate on a beating heart. The defective mitral valve is accessed. It is removed and replaced with a new valve. Tubes are placed for drainage of fluid which might accumulate in or around the heart. The patient is taken off the heart-lung machine. The surgeon assures that the heart is functioning well and the new valve is working in synchronization with the heart. The separated muscles are rearranged and sternum is replaced. The skin incision is stitched using surgical thread.
- Minimally Invasive Surgery
In this surgery, instead of a single big incision, a smaller incision is made on the right side of the chest. The muscles are divided and this is the route of approach to the heart. The surgery can also be performed laparoscopically. 3-4 small incisions are made on the chest. Surgical tools are inserted through these incisions. A video camera is also introduced inside the chest cavity through one incision. This camera helps to visualize the internal organs.
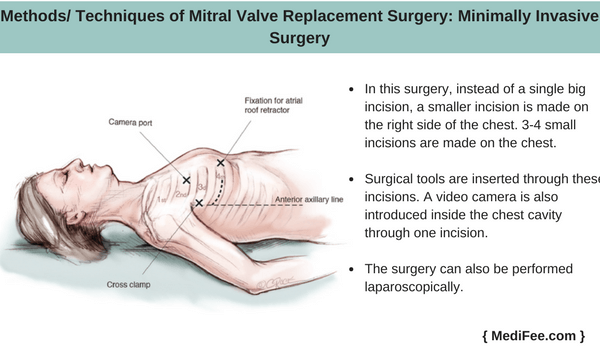
The remaining procedure is the same as described in open surgery. Heart-lung machine is needed in this surgery, but the sternum is not removed.
Post Procedure
On completion of the surgery, the patient is transferred into ICU (Intensive Care Unit). It will take sometime for effects of anesthesia to wear off. After surgery, certain post operative care instructions have to be followed. Some of them are mentioned below.
Immediate CareThe patient is kept under observation in ICU for some time after surgery. Chest tubes which were placed during surgery are checked to drain out any accumulated fluid. As the patient becomes conscious, a general physical examination is done. The surgical incision is checked for pain or bleeding. It is cleaned with antiseptic solution and dressed.
DietA simple diet is to be followed over a time of few days or weeks after surgery. Care has to be taken to avoid weight gain as this will put extra load on the heart. Food containing high cholesterol is to be avoided.
Physical ActivityAfter surgery, it takes about 6-8 weeks for complete recovery. During this span, the patient is to preclude from performing physical activity which involves a lot of exertion as this will put a load on the heart. Also, it might hamper the healing of the surgical incision. At the same time, the patient should not remain completely sedentary (inactive). They should be moving around. After a week or two of surgery, slow walking for a few minutes can be started with the surgeon's advise. This is done so that there is no accumulation of fluids in the body.
Caring for the Surgical IncisionThe surgical incision should be observed and cared for well. It should be cleaned with anti septic solution and covered in surgical dressing regularly. The wound should not be left wet and must be dried properly after bathing. Pain, bleeding or infection at the site of surgical incision should be reported to the surgeon immediately.
After-care methods following surgery, ensure that the patient recovers well and fast. If these are not followed, there could be additional health problems along with delayed recovery.Risks and Complications
The surgical procedure for mitral valve replacement is associated with some risk factors. Though they may not occur in each patient, it is important to know about them and how to deal with them.
- Bleeding:
The heart supplies blood to all organs in human body. During surgery, the blood vessels around heart could be accidentally damaged and there could be bleeding. Blood is removed by draining it through chest tubes. If there is excessive blood loss, transfusion may be required to replenish the lost blood.
- Blood Clots:
After valve replacement surgery, there may be formation of blood clots. This tendency is exacerbated if mechanical valves are used. To avoid this, the patient is kept on blood thinners for long term after surgery. These medicines are however not needed if biological valves are used.
- Swelling:
Accumulation of fluid within the body can lead to swelling of the ankles, at the wrist, face or all over the body. Moving around and performing light physical activity will prevent this. If the swelling is severe and painful, the patient must contact their surgeon. Medicines will be prescribed to reduce the swelling. Blood pressure is also monitored regularly in such patients.

